
Artificial Selection Humans choosing & breeding organisms


Artificial Selection Objectives
-
Compare artificial selection to natural selection.
-
List multiple examples of artificial selection in animal species.
-
Provide possible explanations of how dogs descended from wolves, including the role and possible problems associated with artificial selection.
For thousands of years, humans have known that if you breed two parent organisms with a desired trait, that trait is likely to appear in their offspring.
Artificial selection is humans breeding organisms, selecting for certain traits. Darwin artificially selected pigeons as part of his research. Artificial selection has similarities to natural selection.
Take a few moments to recall the steps of V.I.S.T.A.
We can still use V.I.S.T.A. for artificial selection with a slight modification:
V: there is still variation in organism’s traits, naturally occurring mutations that humans can select to breed.
I: this also depends on inheritance, the genetically-based traits being passed on in eggs and sperm to produce an offspring.
S: in this case humans are doing the selecting of who lives and reproduces.
T.: It still takes time or generations for a trait to become augmented.
A: The species has changed, but the adaptation is to human desired traits, not necessarily the organism’s natural environment.

We’ll use corn as an example of artificial selection throughout the course. Some of the genetics of corn are simple enough for introducing more complex traits observed in animals.
Humans directly use a small percentage of animals, and those species are often selectively bred for desired traits.
Human Uses of Animals

Food
Although humans have largely been herbivores (eating plants) outside of the coldest and hottest ecosystems, animal consumption has increased globally in the past century.

Fiber
Fibers, animal hairs, have been used extensively in human clothing and bedding. Sheep, llama, and alpaca have been bred for hairs with particular qualities.

Labor
Horses, donkeys, and ox have played a key role in agriculture for over 1000 years. Although agriculture has become more mechanized in the past 150 years, animal labor is still significant globally.

Entertainment
Humans have kept other animals as pets for centuries, but the practice has become more common in the past century. In some cases, people describe pets as family members.
There are a variety of other less common direct uses of animals including tissue used as fuels (whale blubber) and organs as sources of medicine or perfume ingredients.
But animals also play an important indirect role in human survival. This means we do not directly use or control the animals, but they are still important to use.
Try to come up with two examples of animals being indirectly important to humans.
How did you do? There are a wide variety of indirect uses, including pollination and parasite control.

Pollination
Bee, butterflies, and some birds, flies, and moth are critical in pollinating many plants. Soybeans, a key human food, are dependent on bee pollinators.

Parasite Control
Small lady beetle (ladybug) adults can eat dozens of aphid plant parasites a day. Birds and spiders can reduce disease-carrying mosquito populations.
We live across the road from these cows; it’s the same for many people in the world, there are now close to 1.5 billion cows on Earth.
Cows are bred for large muscles as a human food (meat), but almost every part of cows are used, including cow skin (cowhides) as clothing, and brain/spinal cord as a filler in pills.
Some cow breeds, bred for strength, have been used as a labor animal for centuries.
Cows (also called cattle) have the scientific name Bos taurus, and descended from large wild cattle of Europe, Asia, and North Africa.


Cows ferment plant material in their stomachs. There are now so many cows on Earth, the methane they produce (through belching) is considered to be a significant greenhouse gas. These are the gases, including carbon dioxide, that impact climate.
Now we’ll take a closer look at dog breeds as an example of artificial selection that has been underway for thousands of years.
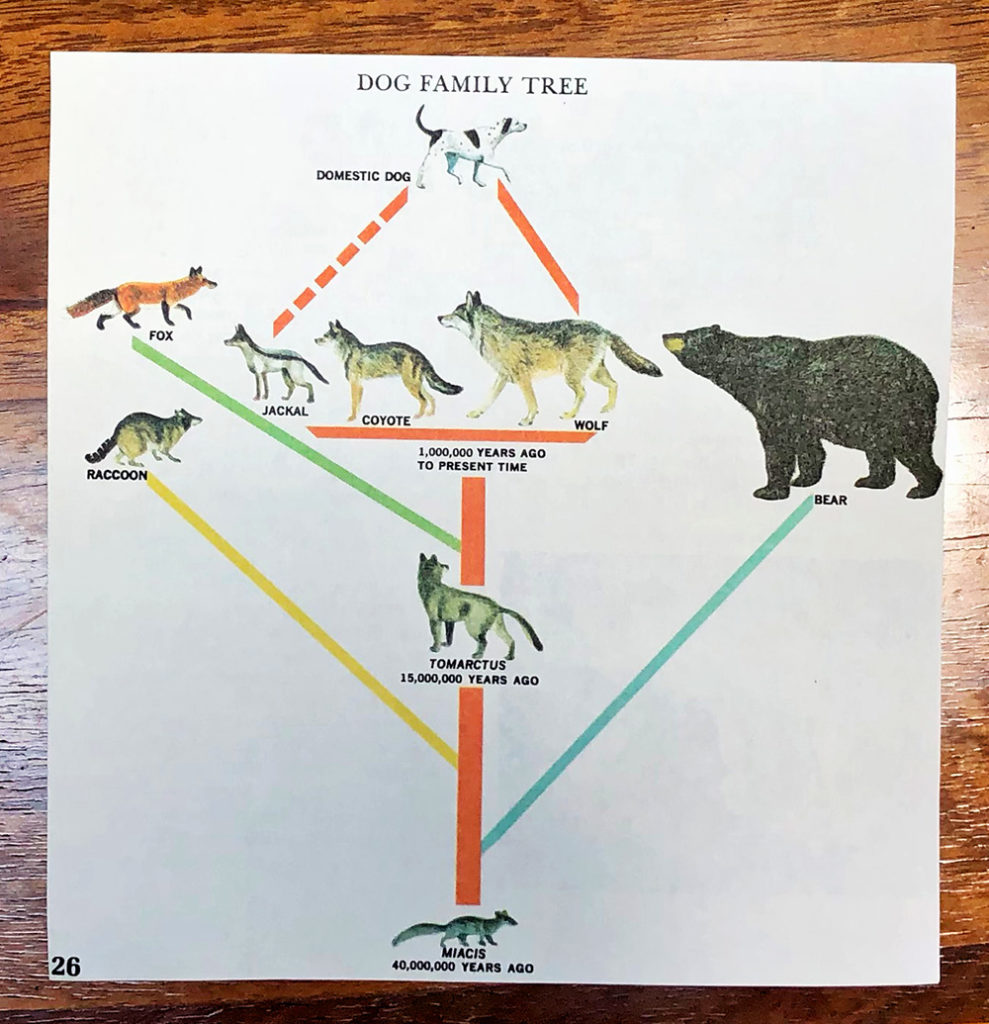
Dogs are descendants of wolves, although the actual original wolf species is still being determined by comparing the DNA of living wolf species to dogs.


There is debate over whether humans selected calmer wolves to breed, or whether calmer wolves were able to creep close to humans to eat available food wastes. Either way, the dog descendants are considerable calmer that wolves.
“Calmer” behavior may have a genetic basis, a lower amount of adrenaline. Interestingly, this may explain why dog colors and patterns are so much more varied in dogs than wolves. Changes in adrenaline and various hormones may impact protein expression of visible traits like coat color.
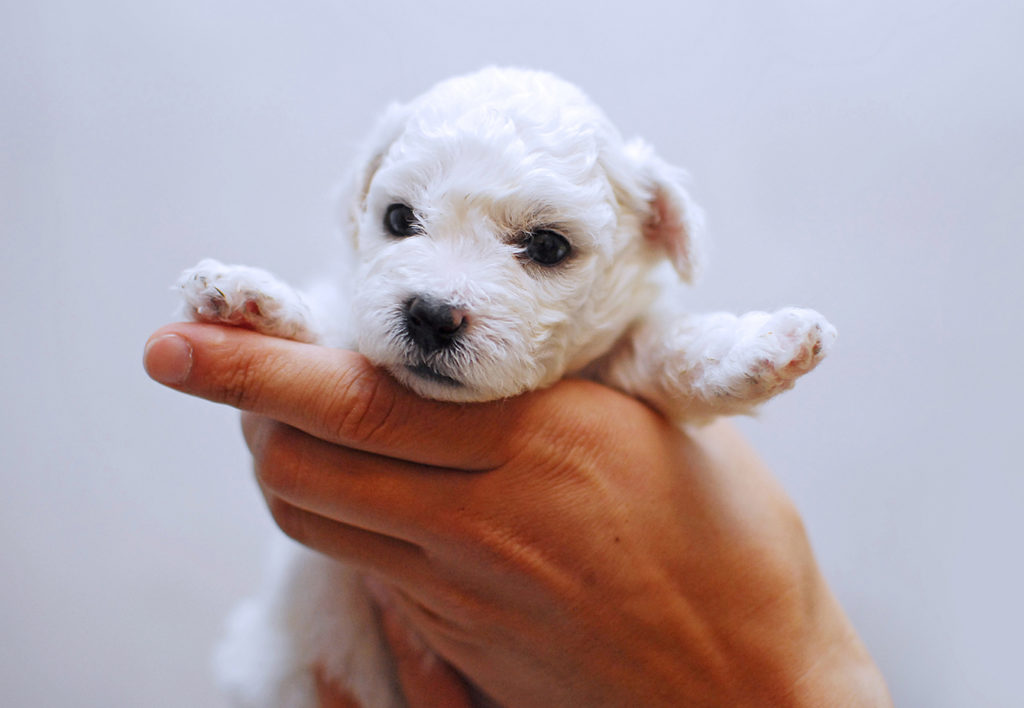


Dogs retain some of the behaviors of their ancestral wolves, including a pack behavior with a dominance hierarchy. Dogs imprint, or learn certain behaviors at a young age, when they are puppies. This includes recognizing family members, one of the reasons for handling puppies in their first few months of life.
Initially dog breeds were largely bred for hunting and protection. More recently dogs have been bred to “breed standards.” Issues have resulted, including dogs that have narcolepsy (falling asleep at inappropriate times), arthritis (joint inflammation), heart disease, and shortened life spans.
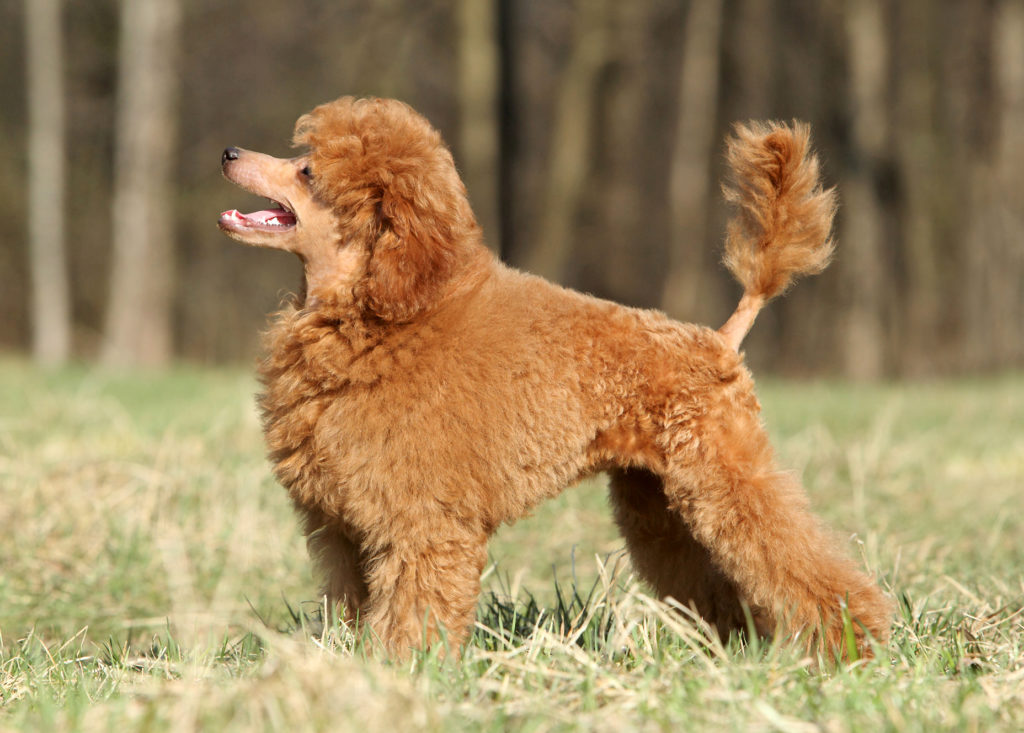

Artificial selection has led to diverse dog breeds.
(source: Shutterstock photos)

This video examines some of the features that are selectively enhanced in dog breeds.
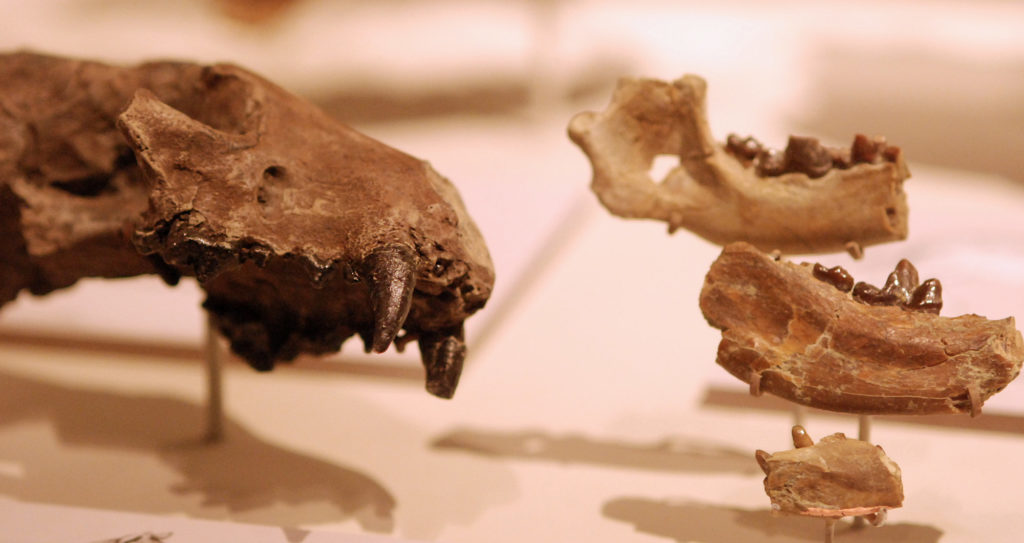

Dog ancestry is studied in part through modern genetic analysis of DNA, and in part through the fossilized remains of ancient wolves and dogs.
Many dog lineages (lines) have gone extinct over time, including at least three different groups of dogs that ranged North America in packs like wolves.
Some of the early hypotheses of dog ancestry prior to DNA analysis have been shown to be incorrect. This 1950s textbook illustration proposes the possibility that jackals were in part the ancestors of dogs. The same was thought of the wild dog packs of the African savannah (same common name, completely different species). We are learning that even if two species look alike and behave alike, they could have diferent evolutionary pathways.
“Everything I know I learned from dogs.”
– Nora Roberts (author)
Although humans were selectively breeding organisms, there was still a great deal of confusion about inheritance. The next section explores some of the early ideas and how Mendel’s research clarified inheritance.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
compare artificial selection to natural selection?
-
list multiple examples of artificial selection in animal species?
-
provide possible explanations of how dogs descended from wolves, including the role and possible problems associated with artificial selection?



