
Coevolution Species Through time together


Coevolution Objectives
-
Define coevolution and give examples of species that are impacting each other over time, including origins of eukaryotes.
-
Provide examples of symbiosis, including parasitism, mutualism, and commensalism.
-
Summarize the structural characteristics, representative organisms, and ecosystem significance of cnidarian species.

Species travel through time and space together, impacting each other’s fitness. This Anna’s hummingbird and the flowering sage plant have been together for generations. Interactions are not one-sided, all participants are potentially impacted.
Managing endangered species often involves also maintaining the species they have co-evolved with over time.
Here, one of our geckos has just caught a fly and is retreating with it back into a Dracaena plant, also from Madagascar. The gecko’s fecal material fertilizes the plant, and the plant’s leaves hold water the gecko drinks. Three species are impacting each other: the gecko, fly, and Dracaena. Over time, these species may evolve in part based on these interactions.
This video defines coevolution and provides examples of species changing together over time.
Symbiosis
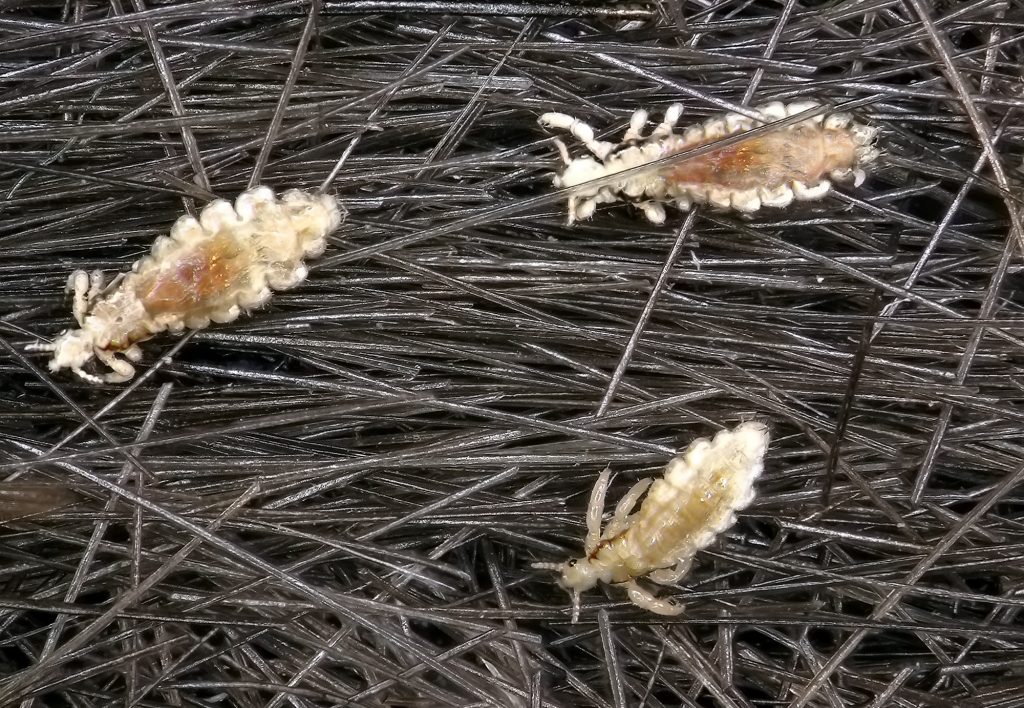

We use the word “symbiosis” in everyday language to mean getting along together, like having a symbiotic relationship with a roommate. In biology, symbiosis means living closely together, sometimes for long periods of time, and the outcome is not necessarily beneficial for all participants.
This video introduces the three major forms of symbiotic relationships.
There is a lot going on in this video: the hermit crab is using a sponge instead of a snail shell for protection. The sponge may or may not be impacted by this arrangement. If its not impacted, but the hermit crab is benefiting, this is an example of ______. The algae growing on the sponge is getting more surface area for growth and possibly additional nutrients, but the sponge it is growing on is not getting as much food into its pores. This example of one species benefiting and the other being harmed is _____.
Cnidarians
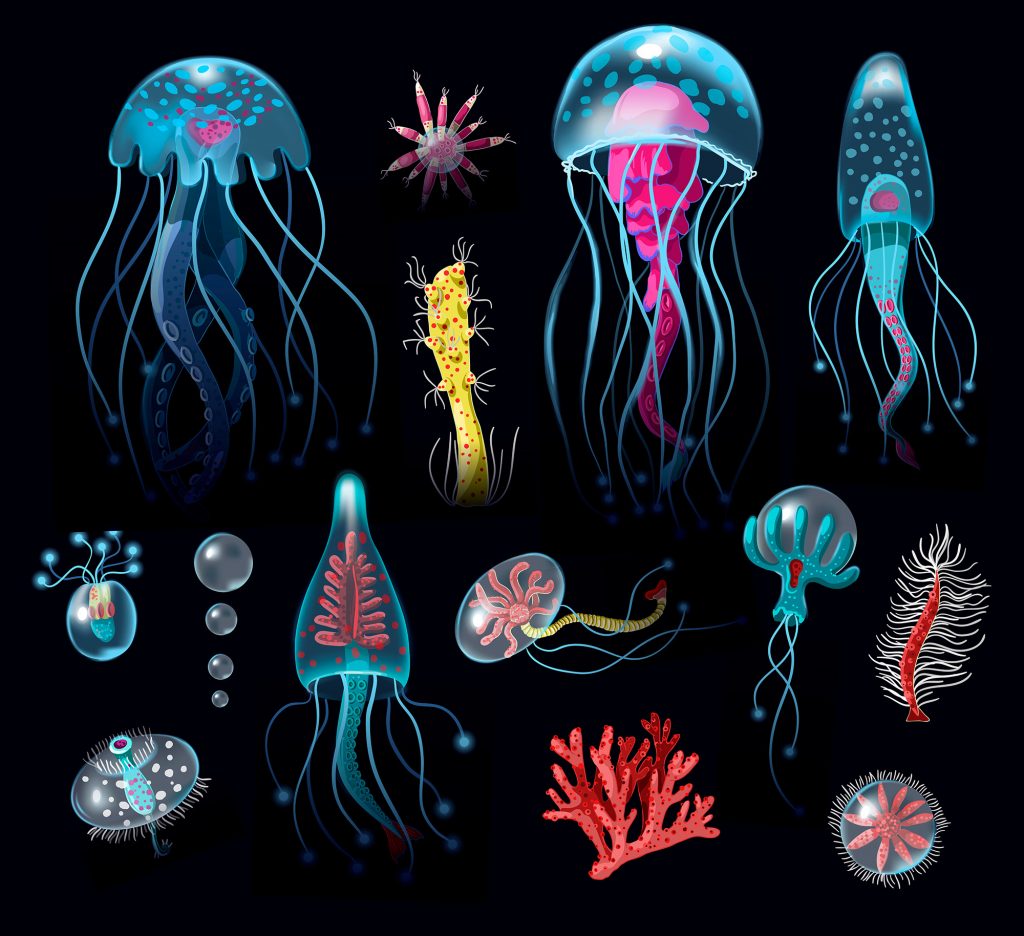
One of the best-known and significant examples of symbiosis and coevolution are the relationship between cnidarians and the microorganisms that live within them.
Phylum Cnidaria includes many well-known marine invertebrate species, including jellyfish, corals, and anemone.
Cnidarians have stinging cells called cnidocytes that have a trigger and a barbed hair-like extension than can inject toxins into potential prey.
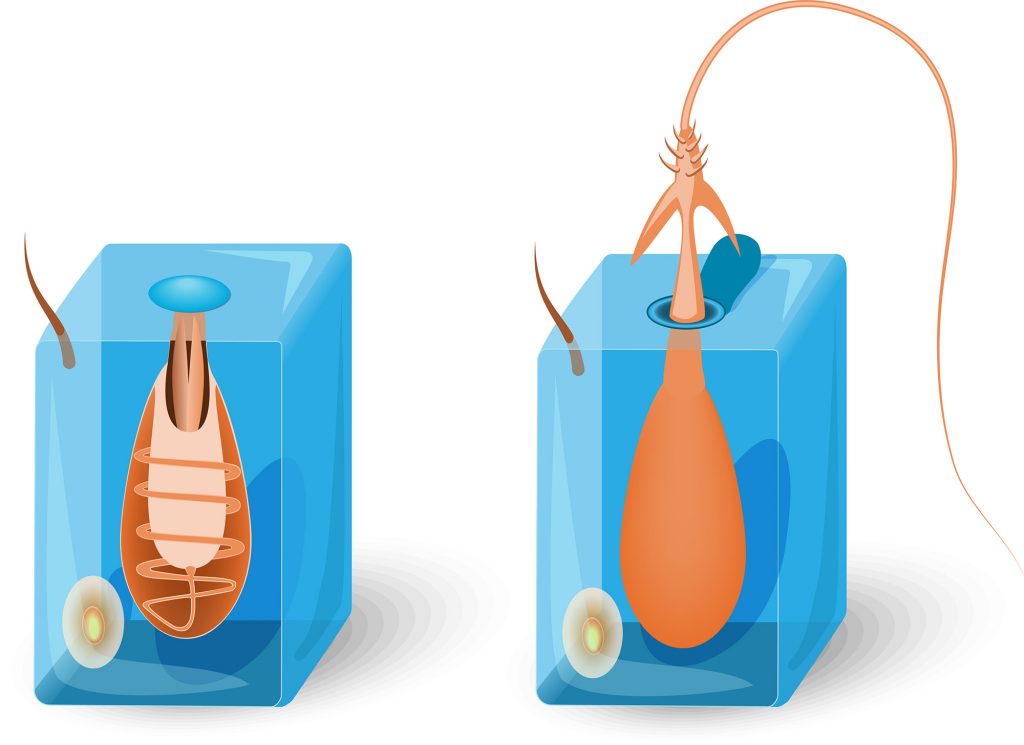

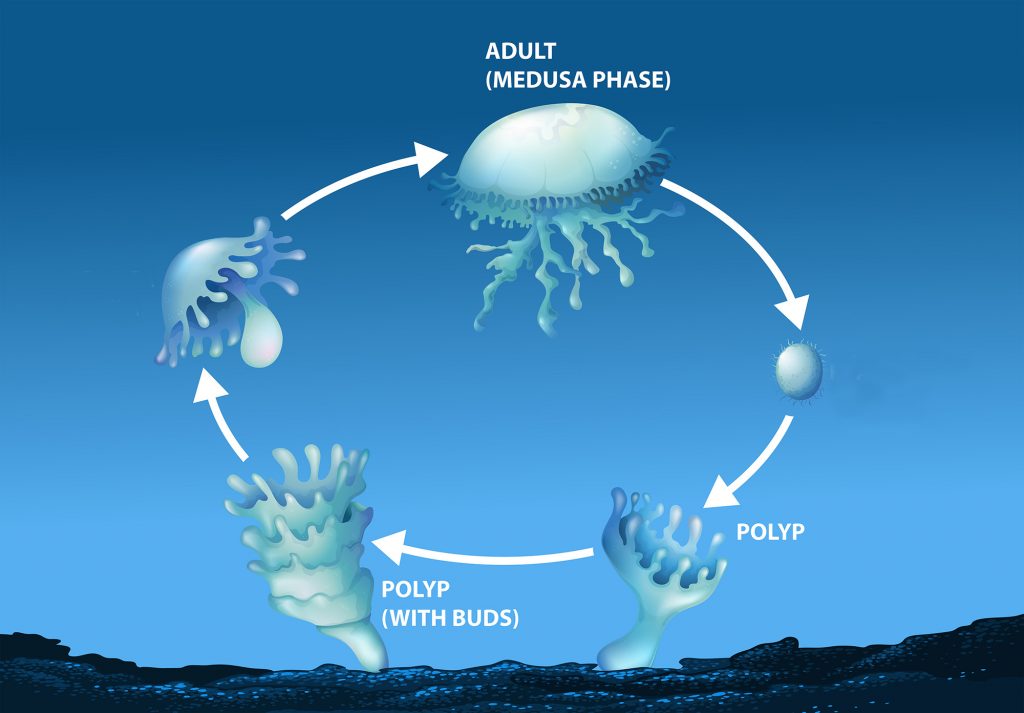
Many cnidarians have a polyp life stage when they are attached to a surface and a free-floating or swimming medusa stage where the body is shaped like a bell with trailing tentacles.
Jellyfish
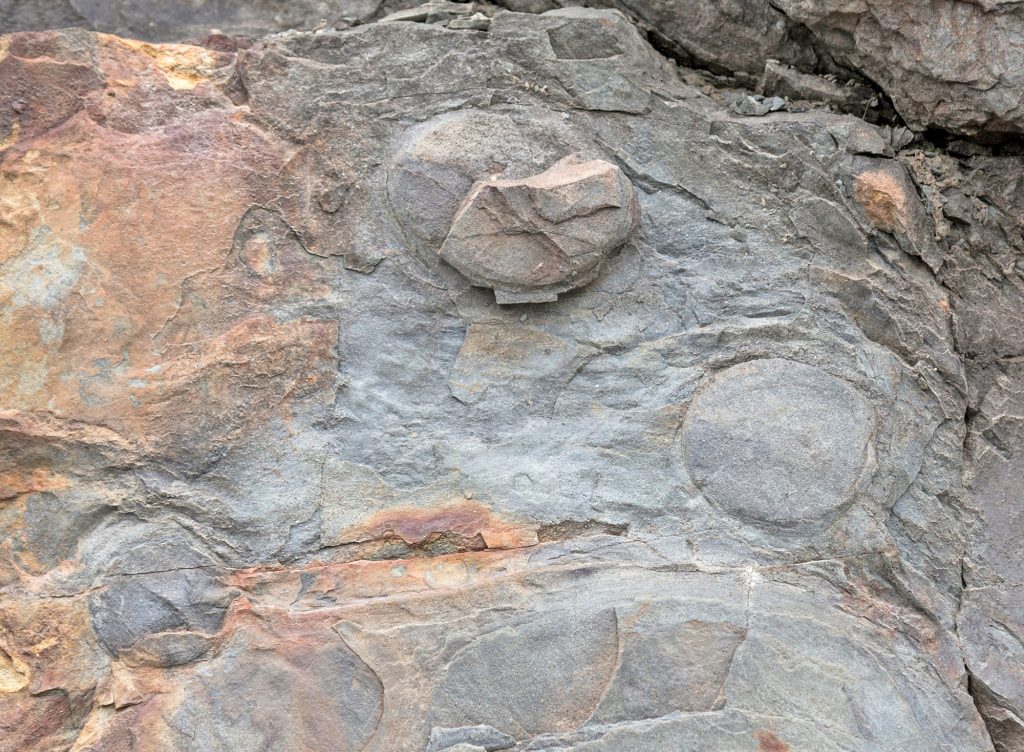

Jellyfish are believed to be the oldest taxa of animals with organs, dating back as far as 700 million years ago. Sponges, animals without organs, go a bit further back in the fossil record.
Jellyfish typically have long tentacles that can catch food flowing through the water. These “upside down” jellyfish (Cassiopeia xamachana) lay bell side down in the sand and catch small organisms out of the water. Their tentacles have endosymbiotic zooxanthellae, and they orient them towards sunlight. The jellyfish get sugars, and the zooxanthellae get shelter and some nutrients from the jellyfish. Both species benefit, so this is an example of a _____ symbiotic relationship.
A group of jellyfish filtering water for food and pointing zooxanthellae-filled tentacles up towards the light.
Corals
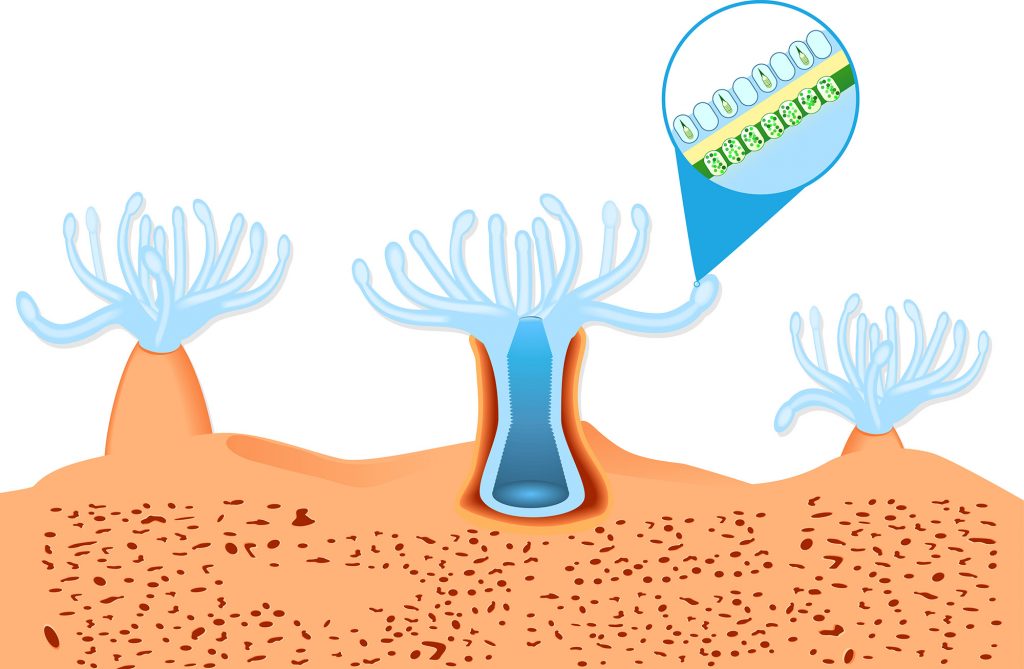
Coral animals have a critical endosymbiont: photosynthetic microorganisms called zooxanthellae.
This video introduces coral animals and the coral reefs they produce.
These videos show two different types of coral species. Both are a group of polyps, and each individual polyp has its own mouth and tentacles.
Anemone
Anemone often have endosymbiotic producers living in their bodies. The anenome species are found in cooler coastal waters, but resemble anemone found in warmer coral reefs.
This touch pool at the Hatfield Marine Science Center in Newport, Oregon is a comfortable way to study and make media about anemone.
Something we teach to the children in our lives: gently handling an organism and describing the process.
Knowledge about cnidarians is needed to develop techniques for stabilizing the complex coral reef ecosystems.
Start this Guide’s second journal page here
Journal Page #12: Cnidarian Tank
Journaling is not only about observing and reflecting on the real world, it is also a place where people plan and “daydream,” thinking of possibilities. Many people think about some day having a marine tank, and cnidarians are often featured organisms. In this assignment you are sketching your own “dream” marine tank with at least two different cnidarian species featured.
You can add other species if you like, fish, decorations, etc. The tank can be any shape or size you want. You can use the videos on this page as references. Have fun with this, journaling can confirm knowledge and be enjoyable.
You are turning in a sketch of a marine tank that includes at least two different cnidarian species. Provide labels or a comment if you think any parts or organisms need additional information or clarification.
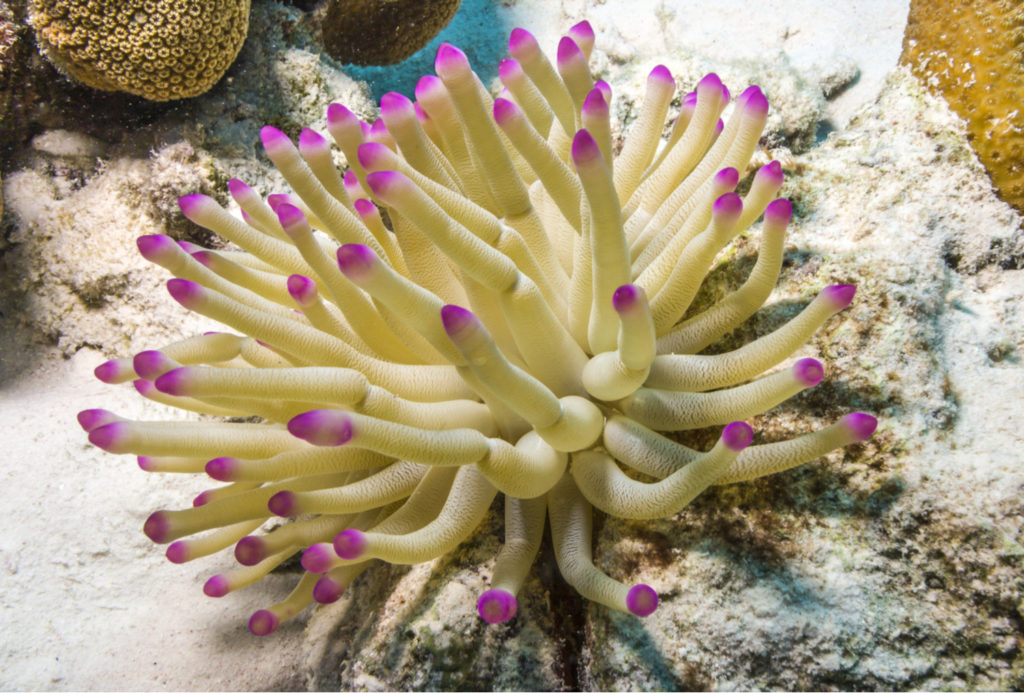

Marine Tank
Thinking of setting up your own marine tank? It can be an expensive hobby and the best way to start is to get educated by people who know what they are doing. Online forums like Reef2Reef have large libraries of information and experts eager to assist. Local clubs often have swaps-and-shares, a great way to get inexpensive or even free invertebrates.
This is the end of the Extinctions Guide content. After you check your knowledge over the material, proceed to the product page.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
define coevolution and give examples of species that are impacting each other over time, including origins of eukaryotes?
-
provide examples of symbiosis, including parasitism, mutualism, and commensalism?
-
summarize the structural characteristics, representative organisms, and ecosystem significance of cnidarian species?



