Marine Producers Protists, Bacteria, & Archaea


Marine Producer Outcomes
-
Provide examples of marine plankton and their roles in food webs.
-
Describe the types of macroscopic producers found in marine habitats.
-
List examples of producer and consumer Protists.
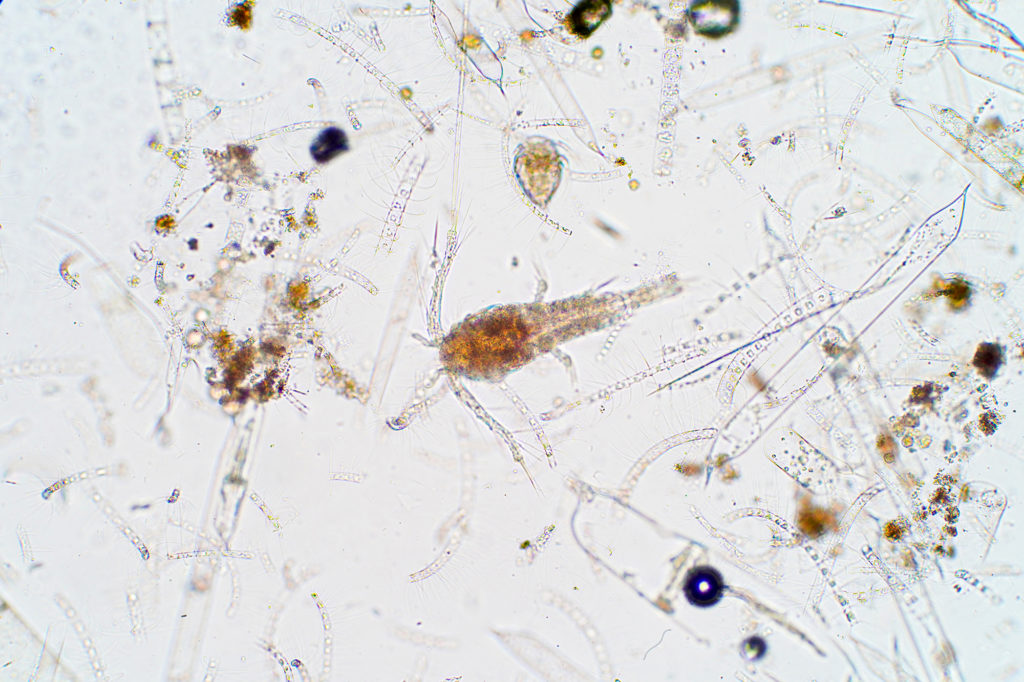
Most marine organisms are quite small and are carried around by waves.
Plankton is the term used to refer to groups of organisms too small to swim against water currents.

The primary producers of the ocean are microscopic phytoplankton, including protists like algae and diatoms.
The majority of marine consumers are planktonic, including protists and small animals.

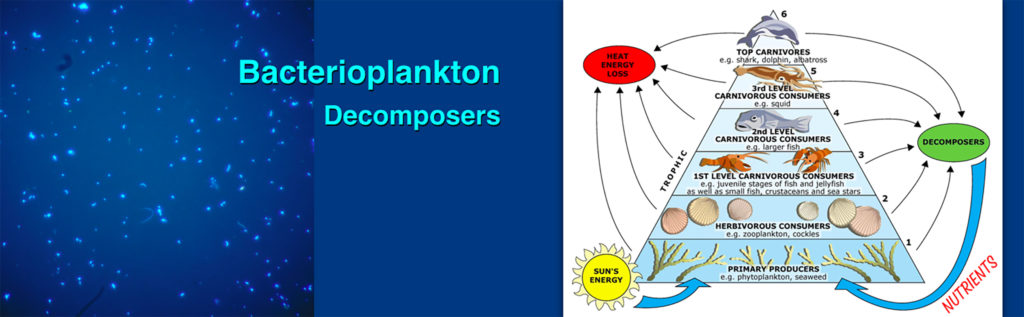
Most decomposition is carried out by species of bacteria, enabling nutrients to cycle back to producers.
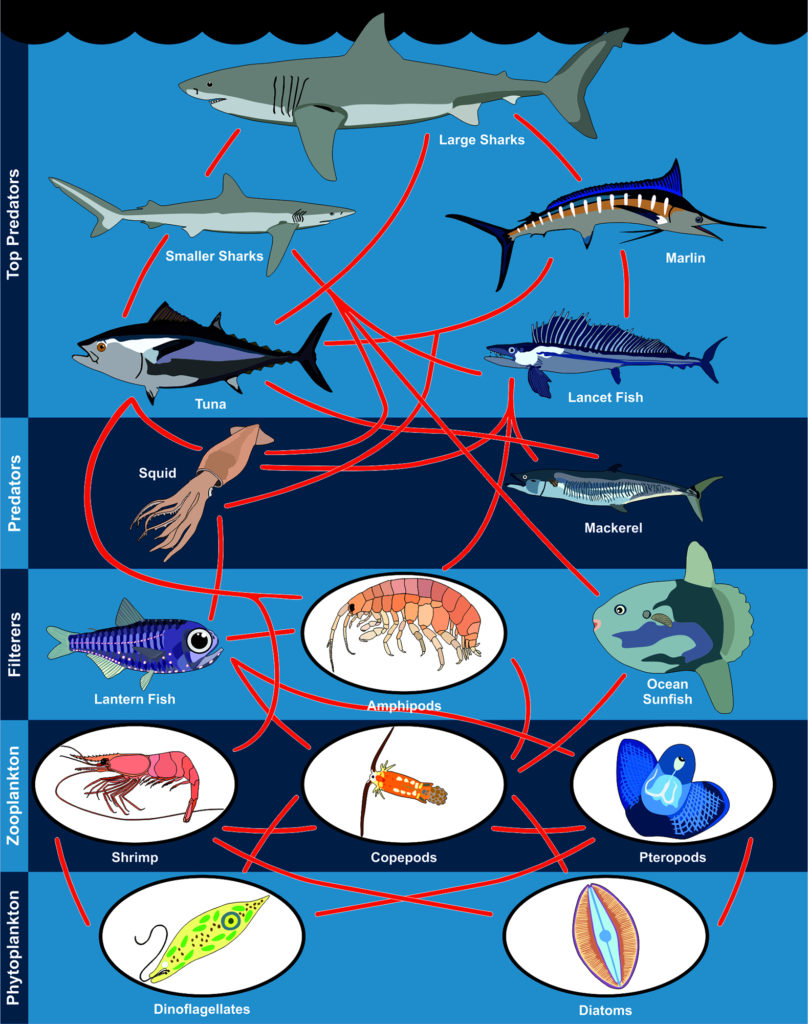
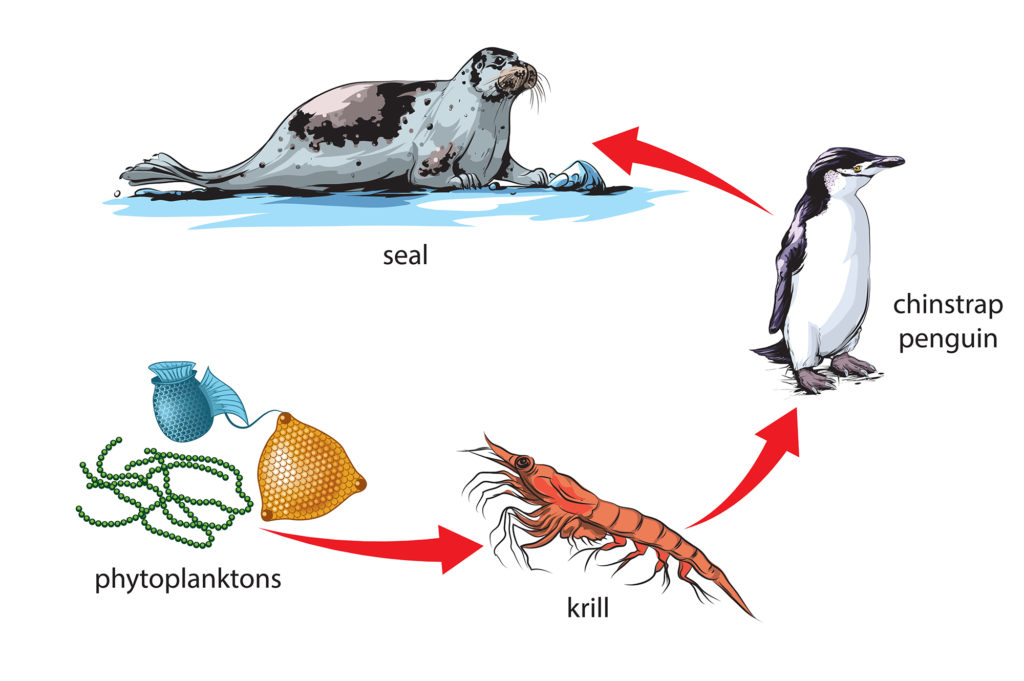
Massive numbers of phytoplankton are needed to support higher trophic (feeding) levels.
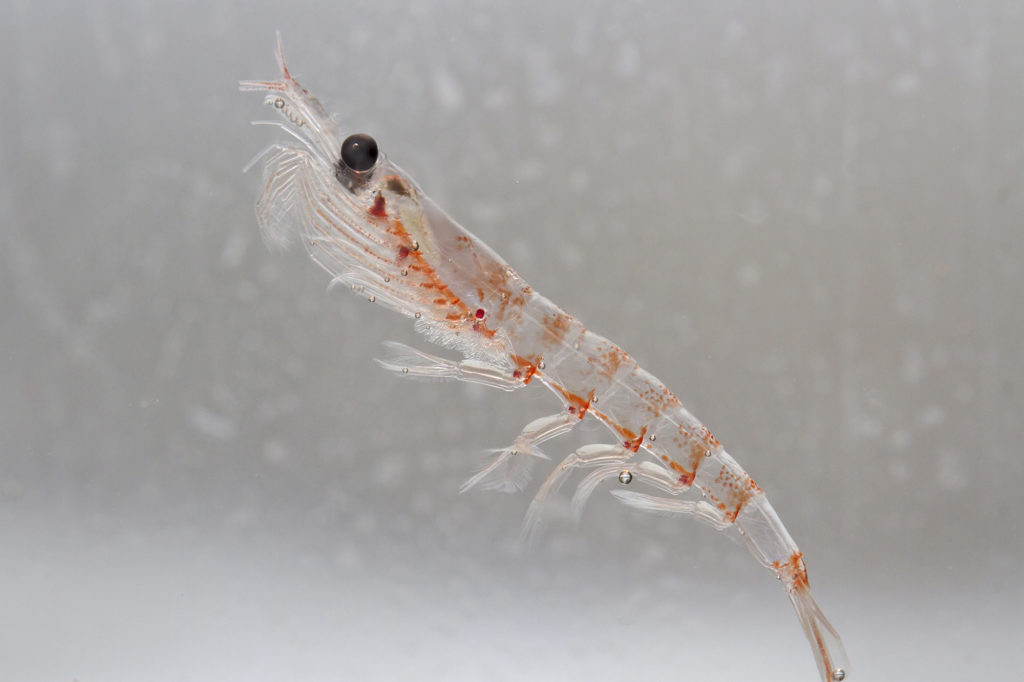
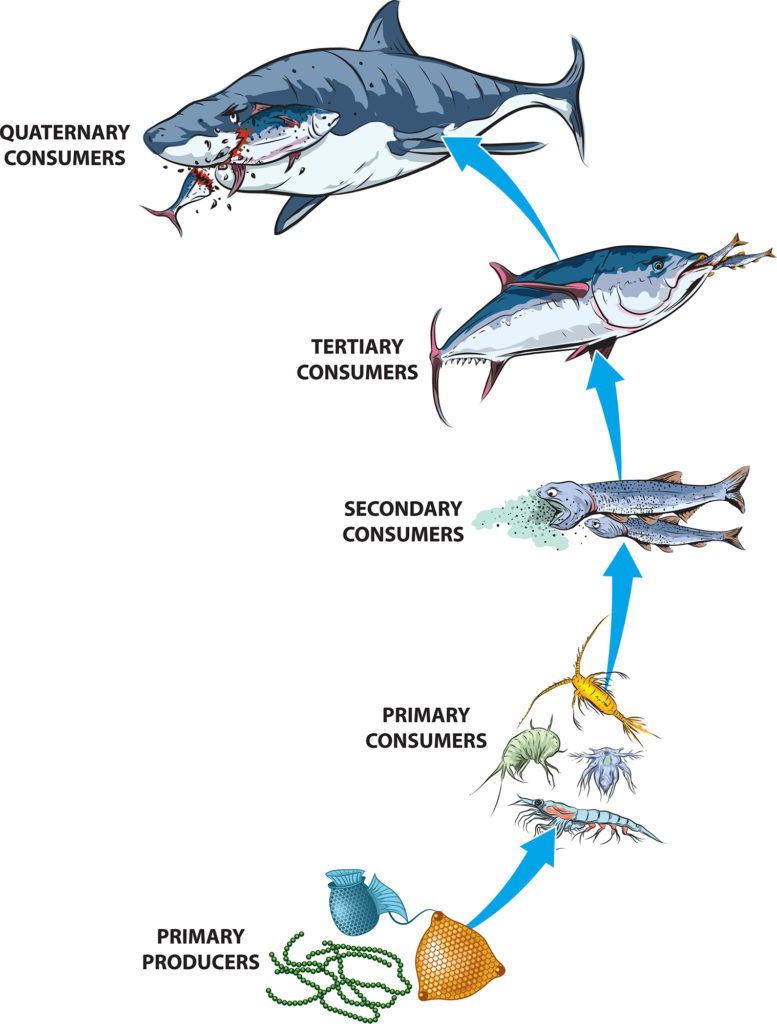

Fluctuations in phytoplankton can impact krill, and many consumers rely of krill as a primary food source.

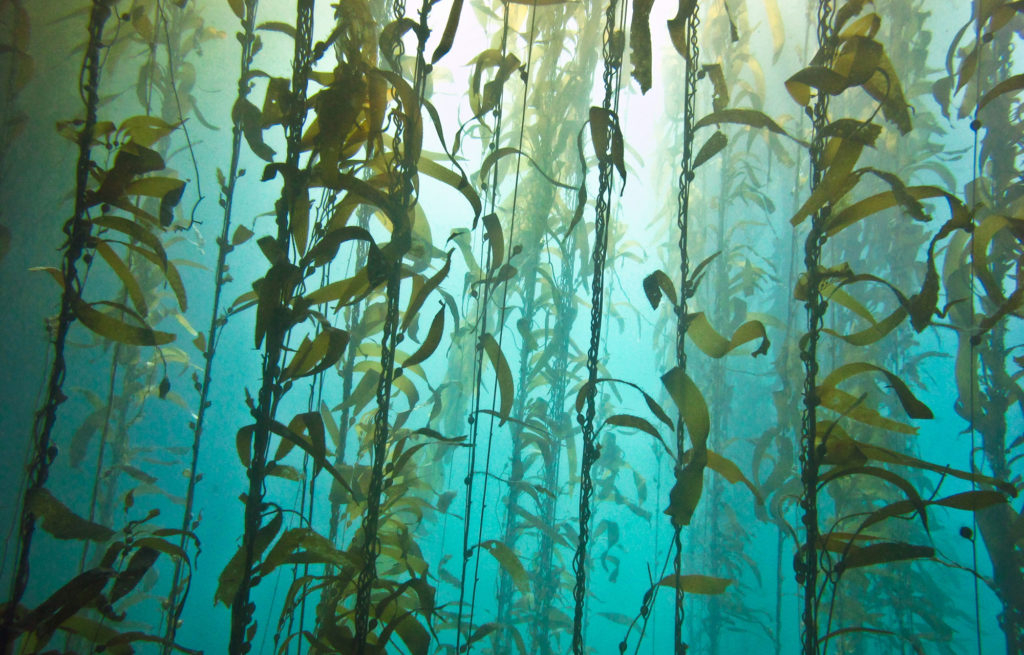
Most marine producers are tiny, but there several notable macro(large) producers including the seaweeds.
Seaweeds are not plants, they are actually large algae. You can tell by squishing fresh seaweed between your fingers: it squishes easily unlike the more structured plants.
Kelp, algae and diatoms are all classified in Domain Eukaryota and Kingdom _____.
Kelp is algae (seaweed) that grows along many coastlines and appears like an underwater forest.
These sea otters have wrapped emerging kelp around their bodies to stay in place as they sleep.
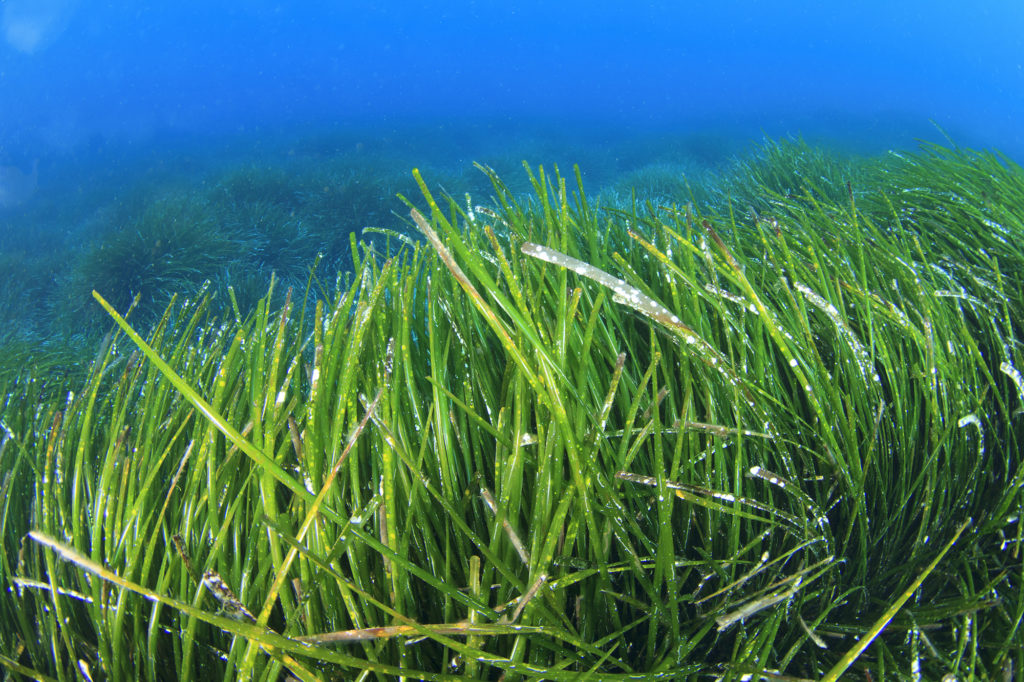


There are some marine plants like this sea grass, but sea plants are primarily found around coastlines. Marine plants are no where near as abundant as algae, diatoms, dinoflagellates, bacteria and archaea producers.
Kelp and other \”seaweeds\” are protists, not plants. We\’re going to take a minute to revisit Kingdom Protista.
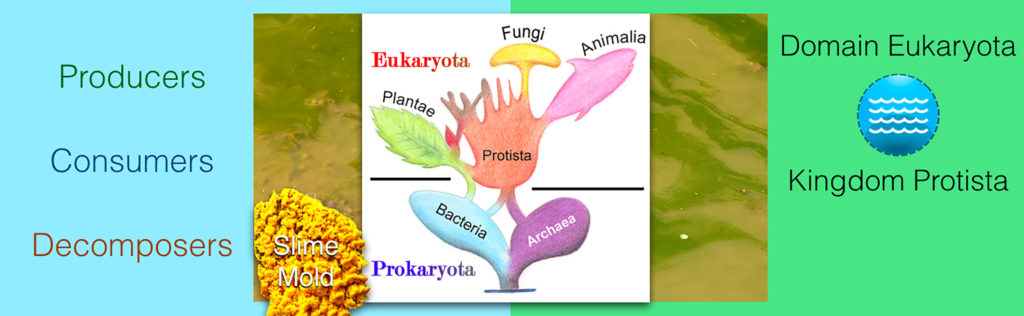
Most Protists are microscopic aquatic producers or consumers. The decomposer species were the relatively uncommon terrestrial slime molds.
Similar to the freshwater pond samples, there are species of algae and diatoms in marine water. Dinoflagellates in saltwater are associated with \”red tides\” of toxic chemicals, but some species play an important mutualistic role with coral animals.

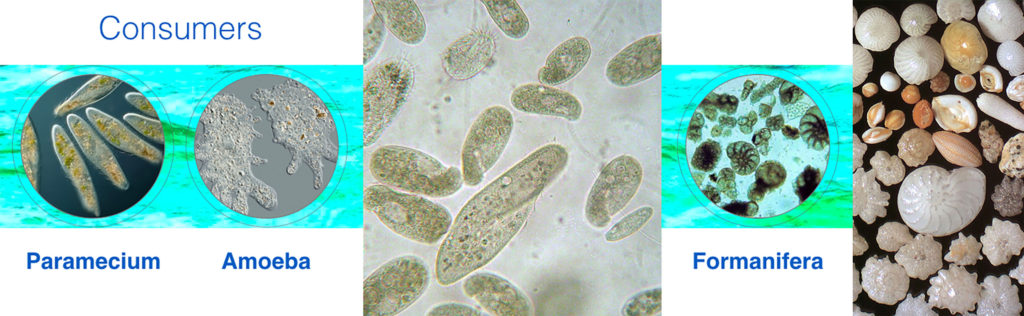
Common freshwater consumer protists include paramecia and amoeba. In saltwater there are many consumer species, including Formanifera that look like tiny snail shells, but are not animals.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
provide examples of marine plankton and their roles in food webs?
-
describe the types of macroscopic producers found in marine habitats?
-
list examples of producer and consumer Protists?