
Parasites & Pathogens Agents that change human history


Parasite & Pathogen Objectives
- Describe different types of intestinal worms, including how they enter the human body and their impact on human hosts.
- List examples of arthropod vector species, and the diseases they transmit to humans.
- Provide examples of diseases caused by fungi, protists, bacteria, and viruses.
This section introduces the parasites and pathogens that cause infectious diseases in humans. Next week we will learn how our bodies defend us against these infectious agents.
We are starting with an overview of the agents (organisms and otherwise) that cause infectious diseases.
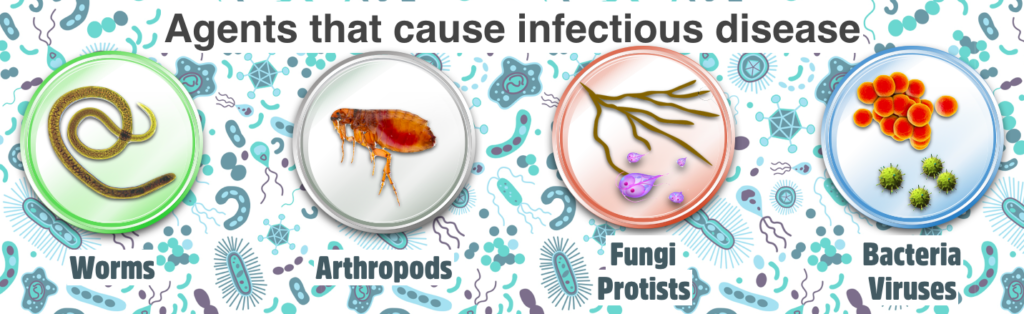
Agents that cause infectious diseases range in size from many feet long (intestinal tapeworms) to smller than a virus (viroids).
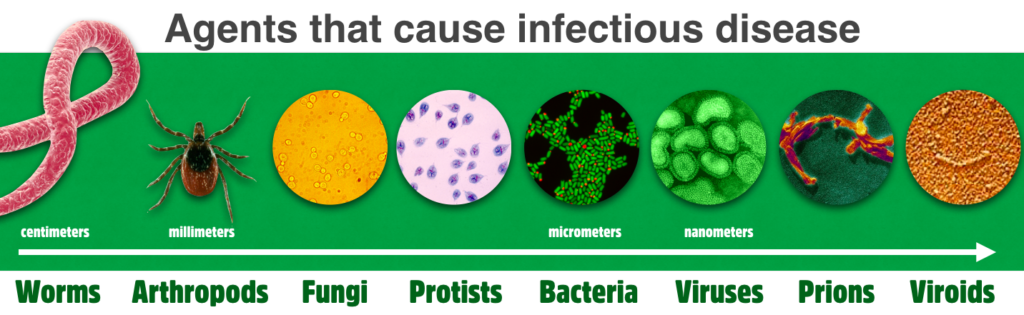
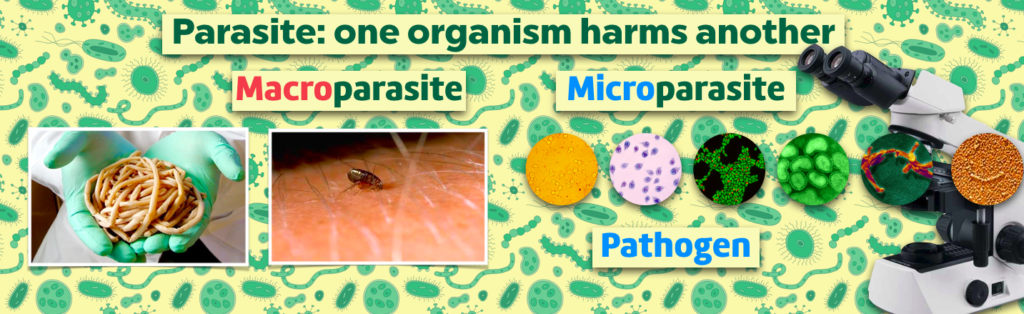
A parasite lives off the body of another organism for food (like a fungus) or as a means of reproducing (like a virus). The ones we can see without magnification are the macroparasites and include worms, arthropods (including insects), and some fungi. The microscopic microparasites are often called pathogens and include yeast fungi, protists, bacteria, and organisms that are too small to live independently without another organism’s cells (viruses, prions, viroids).
Intestinal Worms

Approximately two billion people on Earth are infected with worms. The number is staggering. Clearly these worms are not typically lethal, or we would have heard of these numbers before. However, worms often reside in the intestines, stealing nutrients away from their human hosts. This can lead to malnutrition and an individual becomes more vulnerable to other diseases.
Most worm species are not harmful to humans, some species are beneficial like earthworms. These Planaria flatworms are commonly found in freshwater where they are omnivores and are eaten by larger carnivores. Those big eyespots detect light and are one of their most recognizable features. We keep them as pets.
Now to the parasites.
This video shows how humans become infected, how large the worms get, and their impact on the human population.
It’s time to see real worm specimens, including tapeworms and Ascaris roundworms
Note: some of these worms can be disturbing. If you have had a cat or dog with worms, you know what we are talking about.
Arthropods
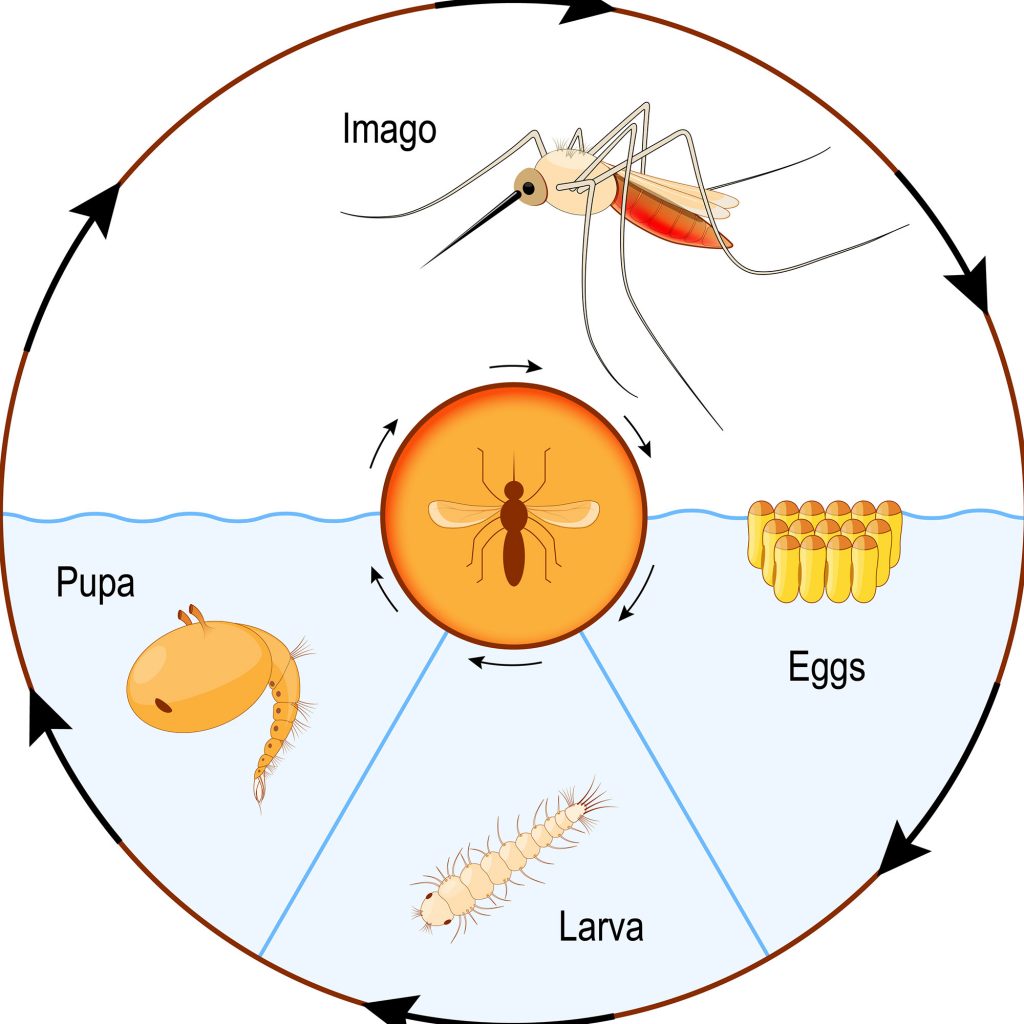
A vector is an animal that can transmit an infectious pathogen, like viruses or bacteria, to humans. If a dog bites a human and incidentally transmits the virus that causes rabies, then that dog would be a vector. However, the most common vectors are arthropods.
This video provides an overview of the significance of arthropod vectors.

Fungi & Protists
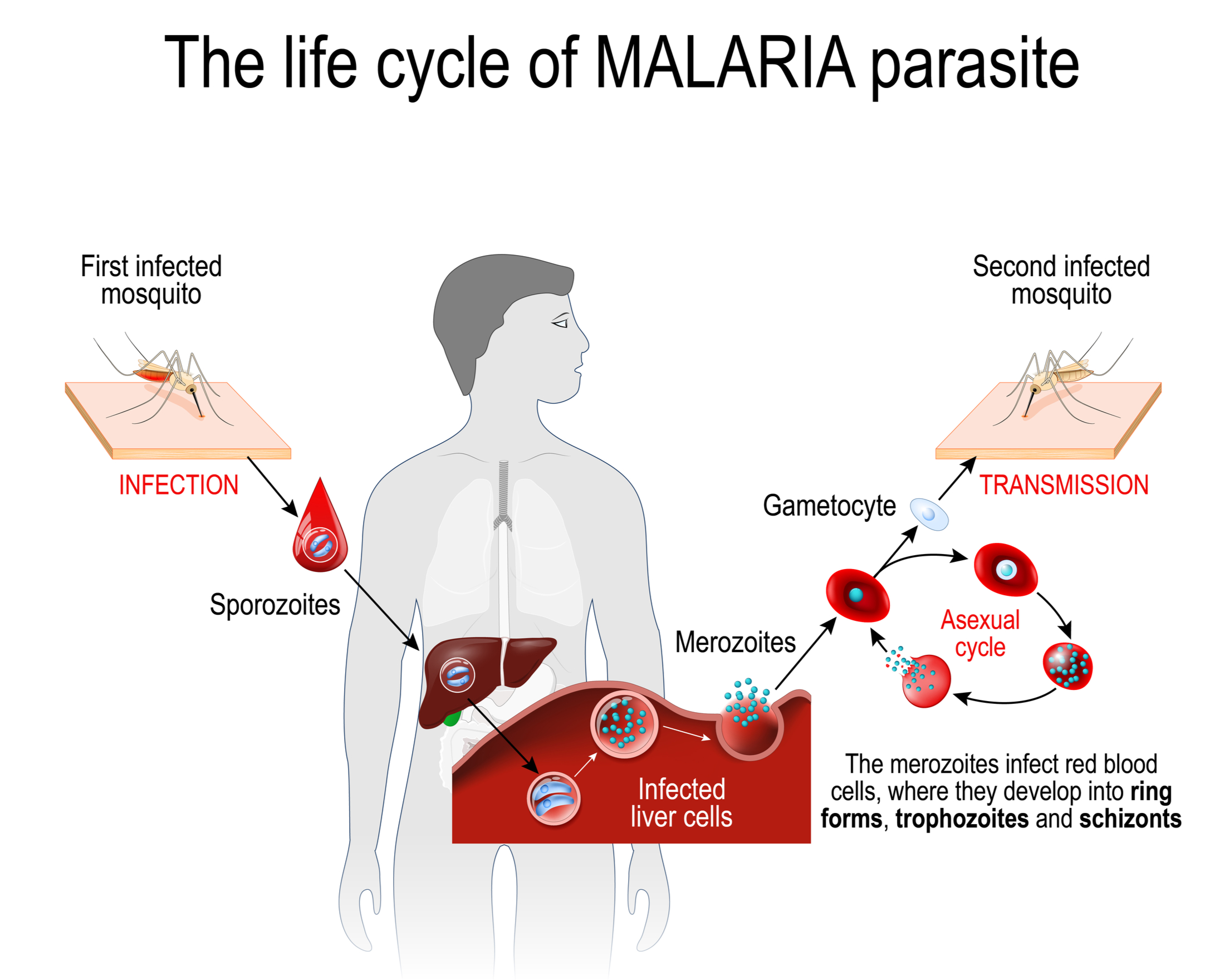
In this section we are meeting some of the fungi and protist organisms that cause disease in humans.
Many people search for information about parasites, pathogens, and infectious diseases, particularly now that we are dealing with a global pandemic. In this section we will also look at sources of science information, including the structure of scientific papers and ways to critique the quality of secondary sources of information.
First, an overview of fungi and protists that cause human disease.
(and yes, those organisms illustrated below really exist! Info is in the video)
This is one species of Aspergillus fungi. Although this group of fungi can cause serious illness in humans, cases are rare relative to the protist-caused disease malaria.

Despite a century of research into malaria, there is no effective vaccine and treatments can be both expensive and difficult to tolerate. The complex life cycle of the Plasmodium protist that causes malaria is part of the the challenge. Another is that the disease occurs most frequently in economically under-developed regions, and until recently the research was poorly funded. Study of malaria is on-going, supported by governments and now also large foundations as well.
Bacteria & Viruses
This is an overview of bacteria and viruses, including two example diseases that show how these pathogens have a significant impact on our species.
Bacteria and viruses impact the human body in different ways. Take note of the three negative impacts bacteria can have, and how viruses impact our cells.
Reviewing your lecture notes, provide an example of each of these different-sized disease-causing agents: worm, arthropod, fungus, protist, bacterium, and virus.
This is the end of Guide 6’s content. After you check your knowledge over the material, proceed to the product page.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
- describe different types of intestinal worms, including how they enter the human body and their impact on human hosts?
- list examples of arthropod vector species, and the diseases they transmit to humans?
- provide examples of diseases caused by fungi, protists, bacteria, and viruses?



