
Immunity Joint Defenses against parasites & Pathogens


Immunity Objectives
-
Provide an overview of various blood cells involved in immunity and their roles.
-
Describe the lymphatic system, including what lymph is and how it travels through the body.
-
List various immune disorders. including immune cancers, immunodeficiency, autoimmune, and hypersensitivity diseases.
In the previous guide, we walked through two non-specific innate defenses and two specific acquired defenses. We will start by reviewing those before talking about disorders.
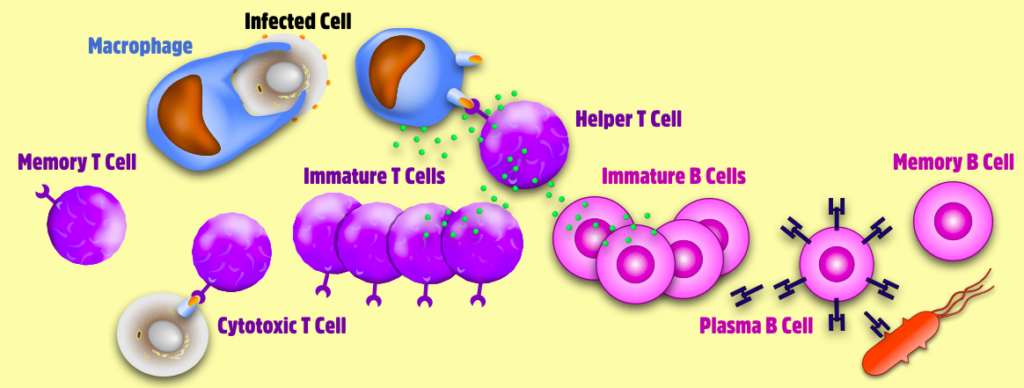
Start this Guide’s first journal assignment here
Journal Page #13: Immune Drawing
Sketch and label the body’s response to a pathogen. Include in your labeled drawing the following 14 components and show what they are doing in the immune response:
wounded cells; cytokines; blood vessel; pathogen; antigen; macrophage; helper T cell; immature (naive) T Cell; cytotoxic T cell; memory T cell; immature B cell; plasma B cell; memory B cell; antibodies
You can have fun with this! We have seen “pac-man” cells, “Mr. T” cells, comic strips, cartoons, mini-plays, and many more creative pieces that have accurately relayed the concepts.
You are turning in an original labeled drawing with all 14 components listed above. Grading is based on cells accurately labeled carrying out their roles within the immune response.
There is an additional video on the resources page that may assist with this assignment.
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system moves lymph, extracellular fluid, back towards the heart, passing through lymph nodes that can filter out pathogens.
Lymph nodes include pockets of lymphocytes that can fight pathogens.
Many people have heard of the spleen, but few can say what it does. The spleen is part lymphatic and part cardiovascular, with roles in controlling red blood cells and antibodies.
Immune Disorders
We are starting with an overview of the major types of immune disorders.
Immune Cancers
Leukemias are cancers that arise in the bone marrow. Bone marrow contains the undifferentiated stem cells that are continually dividing to produce new cells.
Immunodeficiency
In rare instances, babies can be born with an immune system that does not function properly. More commonly, immunodeficiency relates to envieonmental factors and infectious diseases.
Two of the worst-case scenarios are pathogens that attack white blood cells. To make senses of this, a quick review:
The macrophage while it was eating up debris during non-specific inflammation, ripped up pathogens and presented the pathogen’s surface markers (called ___) on their membranes. The macrophages become antigen-presenting cells.
The macrophages communicate chemically with a type of lymphocyte, the ___ T cell, which will tell other B cells and T cells what to kill.
T cells are lymphocytes that left the bone marrow and matured in the ___ gland, located near the heart. B cells are lymphocytes that spent extra time in the ___ ___ maturing.
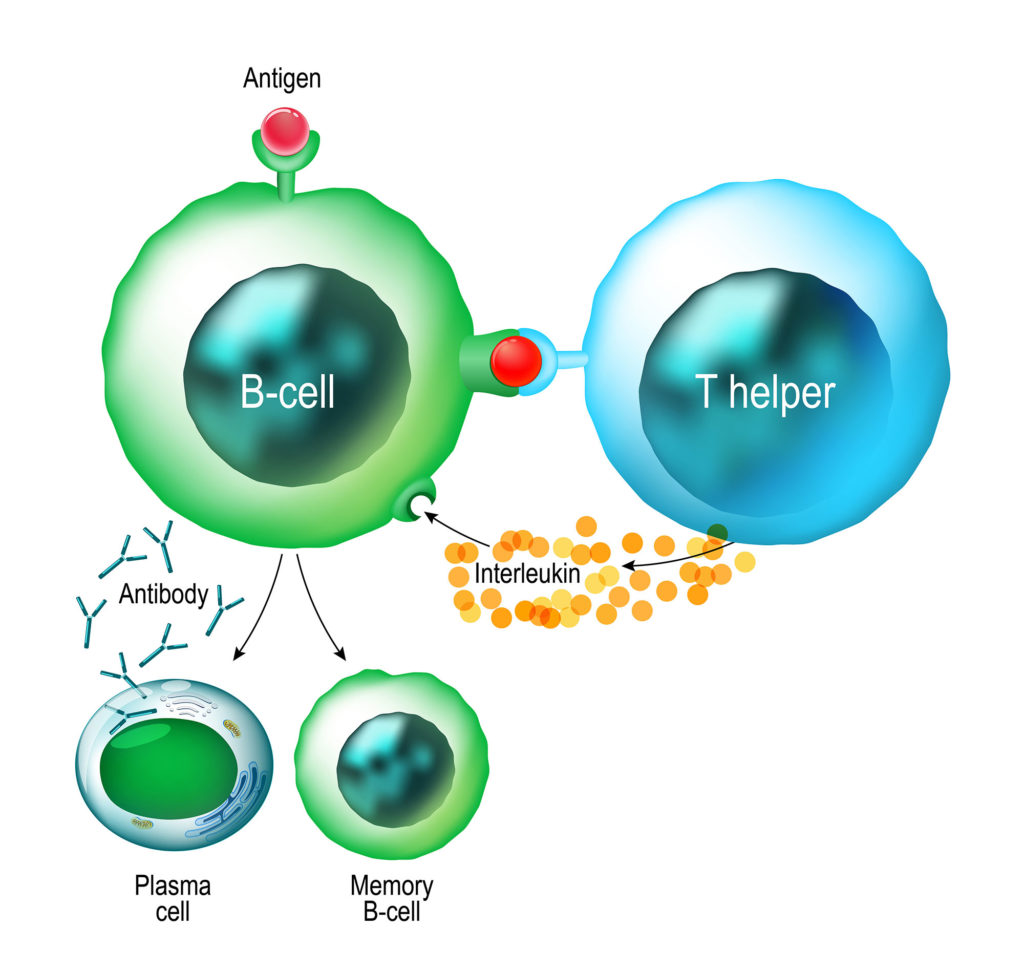

So the last thing you would want are diseases that harm either the macrophage (monocyte) or the helper T cell (lymphocyte). Your body would lose the ability to recognize when it is under attack from pathogens.
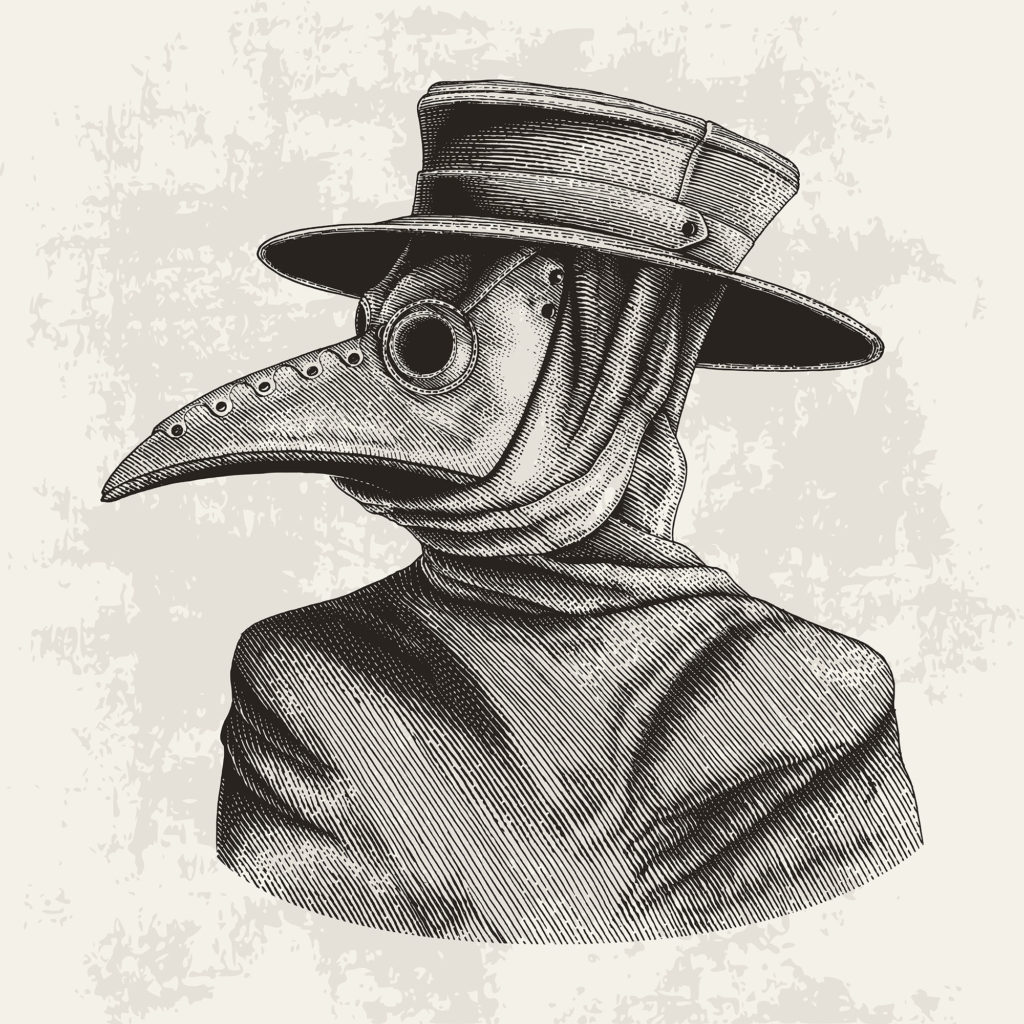
But we have both. The “plague” bacteria Yersinia pestis attacks monocytes and was responsible for killing approximately 1/3 of Europeans in the 14th century and probably many more people on the Asian and African continents. Luckily we now have antibiotics that kill these bacteria.
This is an iconic image of a plague doctor wearing garb to avoid infection.
Unfortunately, HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) attacks a group of helper T cells, interfering with the white blood cells’ abilities to recognize and attack pathogens. Individuals succumb to pathogens their bodies would have otherwise have been able to fight off.
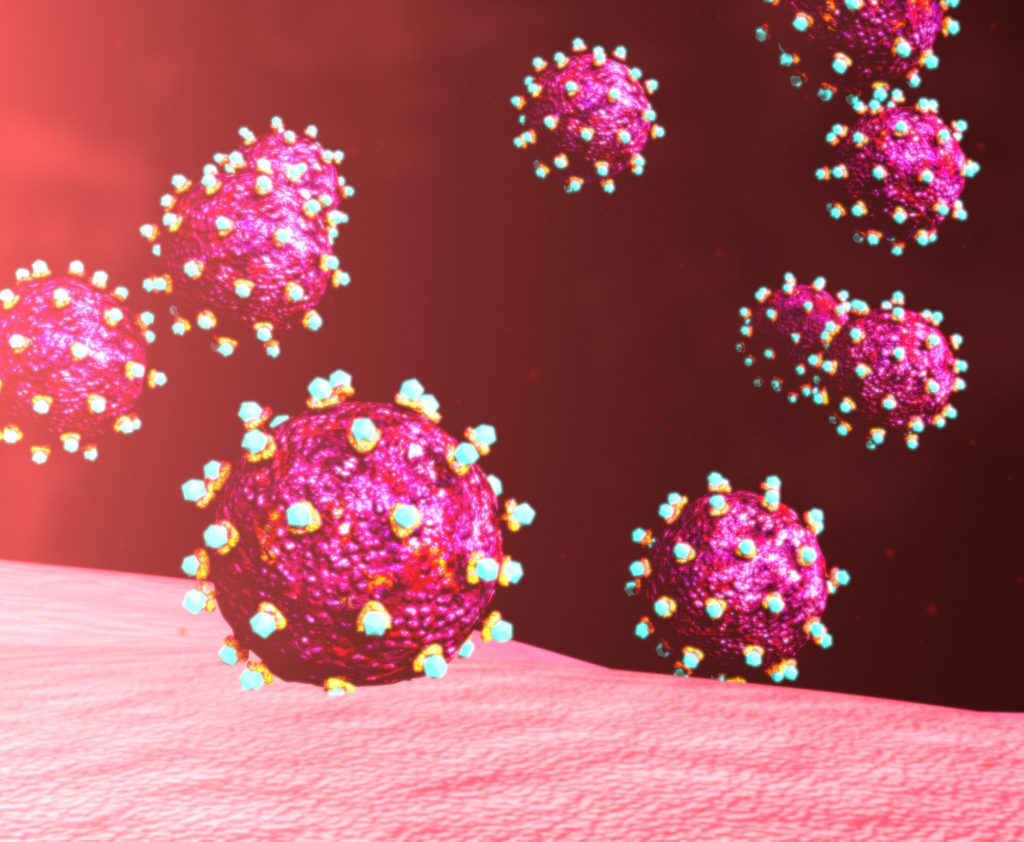
AIDS
HIV leads to severe immunodeficiency by destroying helper T cells.
Autoimmune
In rare instances, babies can be born with an immune system that does not function properly. More commonly, immunodeficiency relates to envieonmental factors and infectious diseases.
We have met three examples of autoimmune diseases already in this course. See if you can recall what they are.
This video provides an introduction to autoimmune diseases.
Managing autoimmune diseases can be challenging, and the diseases themselves are often a mystery to people.
Hypersensitivity
In rare instances, babies can be born with an immune system that does not function properly. More commonly, immunodeficiency relates to environmental factors and infectious diseases.
We will begin with an overview of the most common hypersensitivity disorder: allergies.
Primary exposure to an allergen primes mast cells to respond when re-exposed to the allergen.
The next section introduces how we use medical advancements to control and even eradicate infectious diseases.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
provide an overview of various blood cells involved in immunity and their roles?
-
describe the lymphatic system, including what lymph is and how it travels through the body?
-
list various immune disorders. including immune cancers, immunodeficiency, autoimmune, and hypersensitivity diseases?



