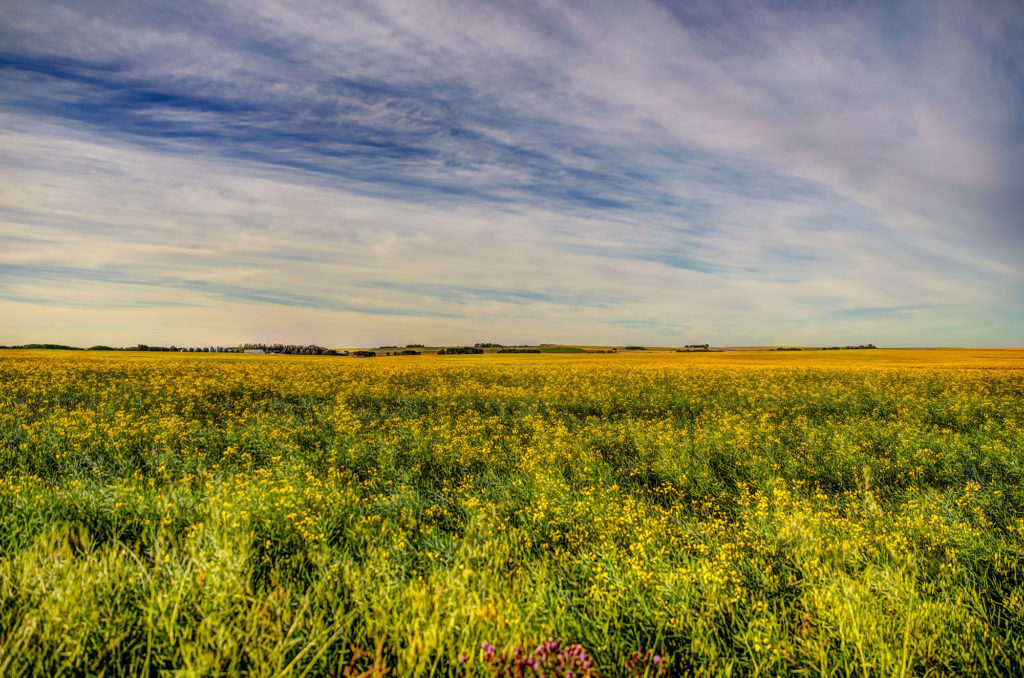
Grasslands Too Dry for Forests; Too Wet for Deserts


Grassland Outcomes
-
List characteristics of grass plants.
-
Describe the climate characteristics of temperate grasslands, and provide examples in different parts of the world.
-
Describe the climate characteristics of tropical savannas, and the role of fire in grassland ecosystems.
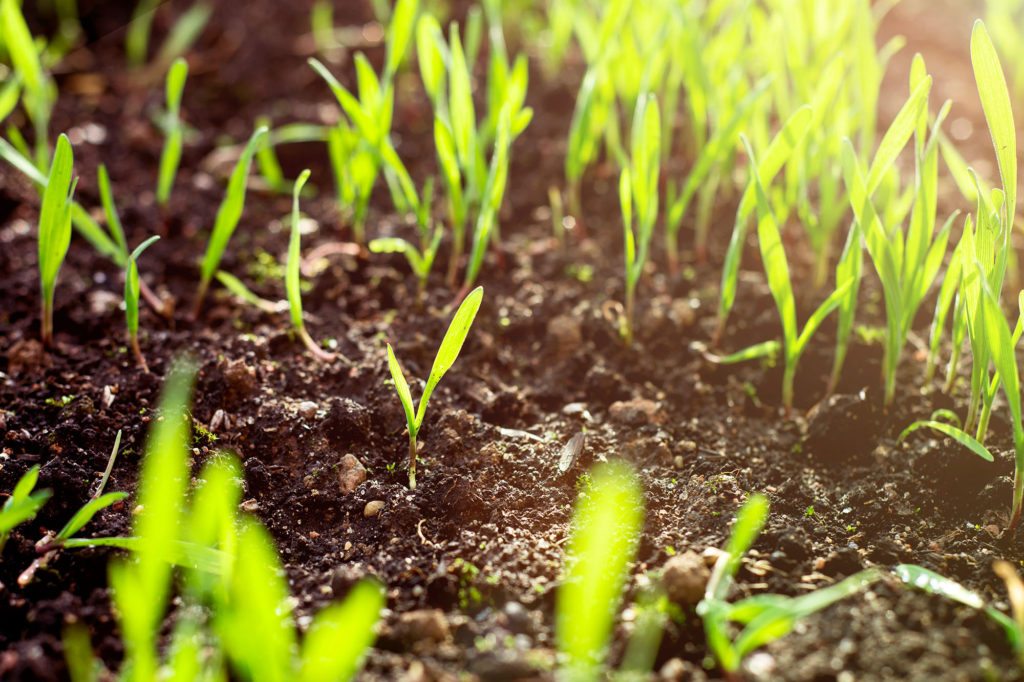

Grass plants are thousands of species classified in Family Poaceae. They typically share thin leaves (\”blades\”) as well as wind pollination and small flowers.
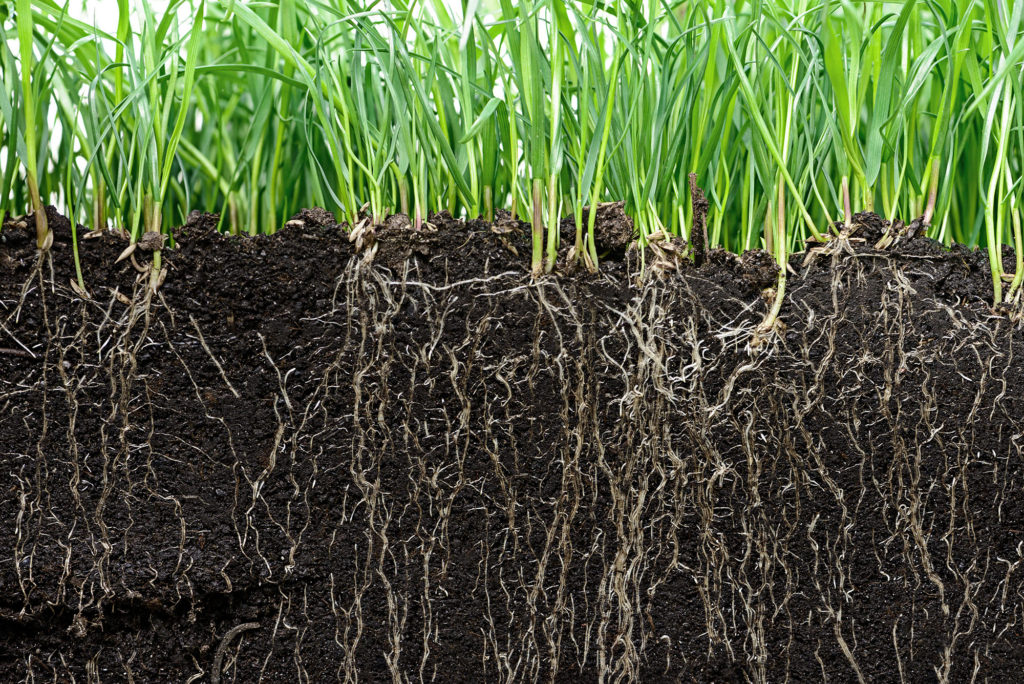

Grass plants have fibrous roots that can re-sprout blades if the plant is eaten by an herbivore, scorched by sun, or burnt by fire.

Many species of grass plants can also tolerate both flood and drought conditions.


Our species directly consumes grains like wheat rice and corn, as well as sugar from sugar cane. We also eat animals that eat grasses, use grass as a building material (in bales), and as a combustible fuel.
Temperate Grasslands
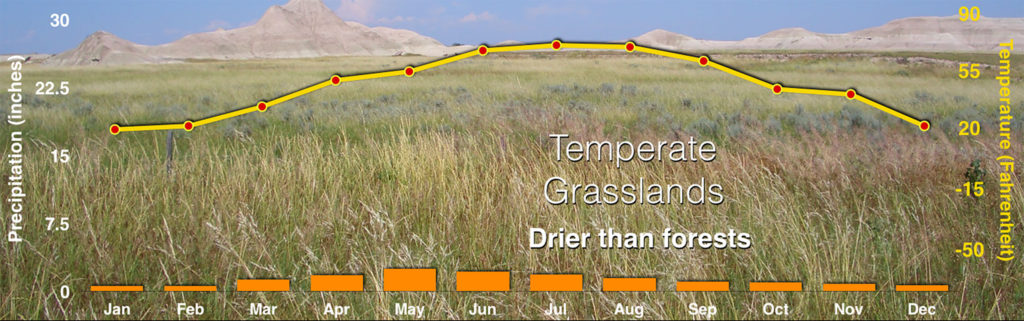
Temperate, meaning \”not too hot or too cold; not too hot or too dry,\” grasslands are typically found in climate conditions somewhere between a desert and a forest. Much of the swaths of temperate grasslands on this general biomes map have been converted to agricultural use.
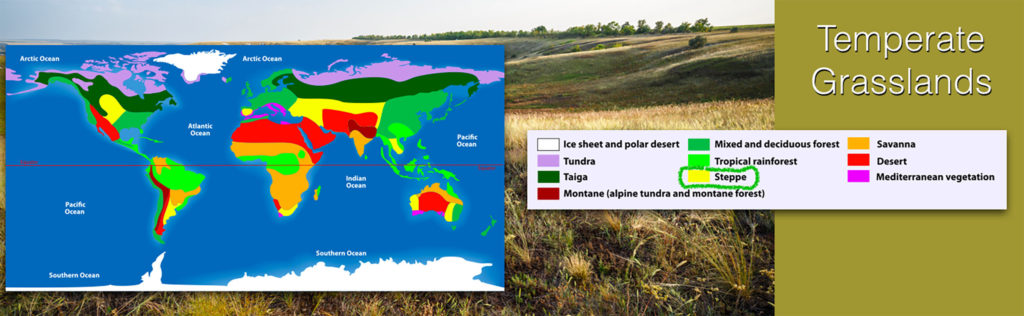
There is enough moisture for grasses, but it is too dry to sustain many, if any, trees.
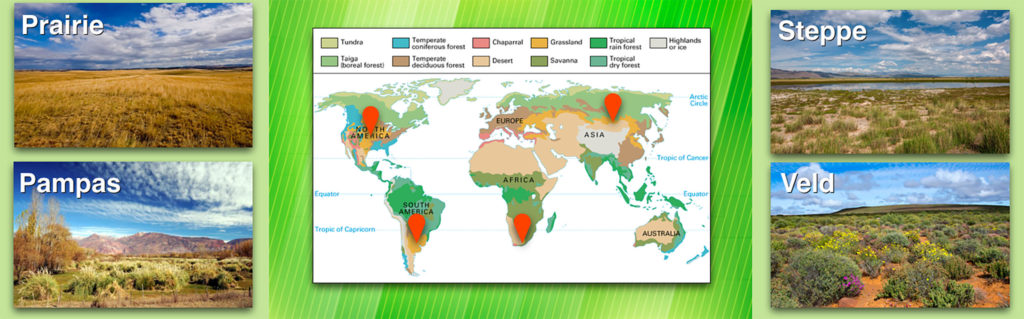
Temperate grasslands have many names, including:
North America: Prairie
Asia: Steppe (these are the largest temperate grasslands, so Steppe is how much of the world refers to these ecosystems)
South Africa: Veld (also spelled veldt)
South America: Pampas
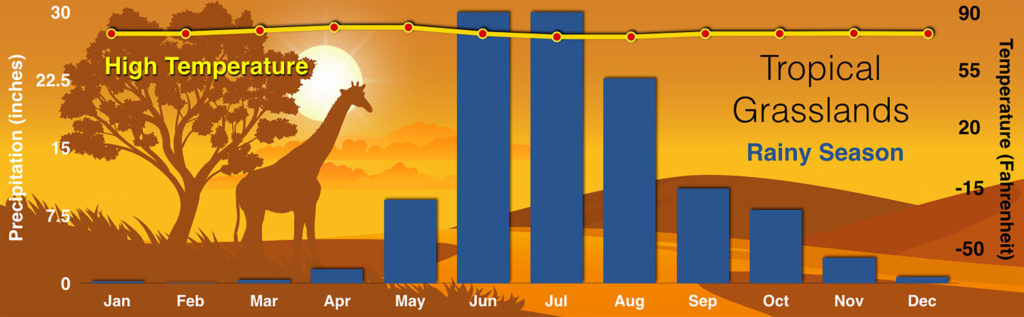
Tropical Savannas
Tropical savannas are found above and below the equator, often bordering tropical rainforests.
Savanna indicates that there are occasionally trees in the grasslands, but they typically have quite a bit of distance between them due to limited water.
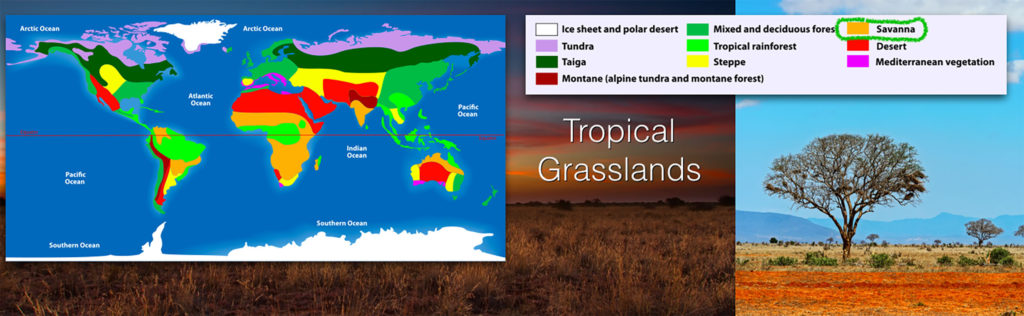
Like tropical rainforests, it is warm all year, but unlike rainforests, there is a dry season and a rainy season.
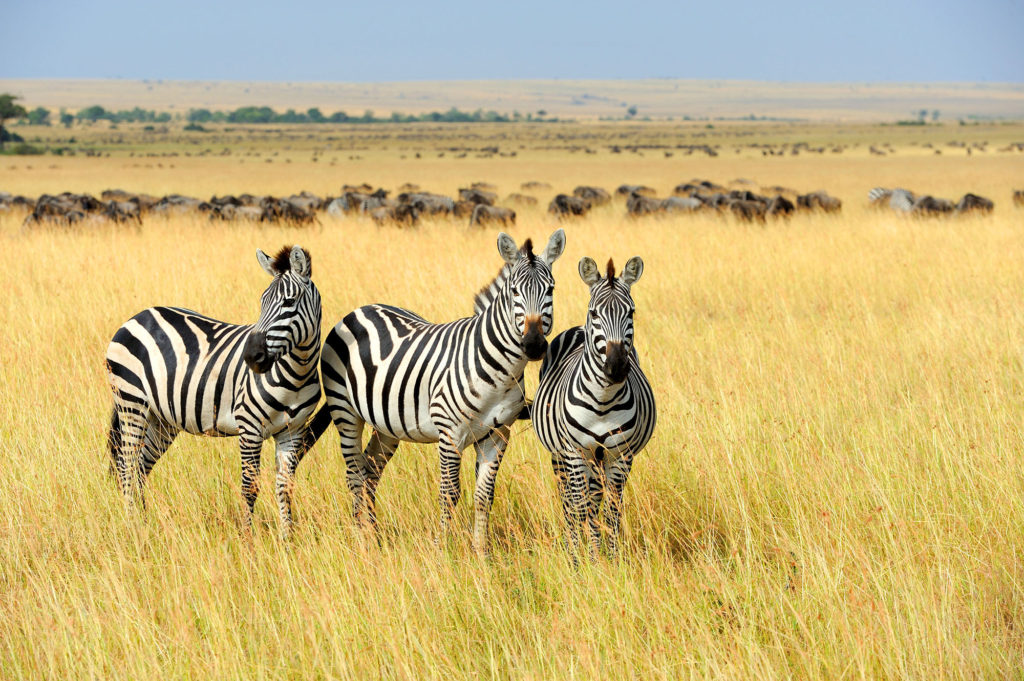

Most of the large wild herds of herbivores that grazed on temperate and tropical grasses are now gone. The exception are the large herbivores that remain in regions of the African continent.
This video describes why savannas in both temperate and tropical climates are dominated by grasses and not trees.
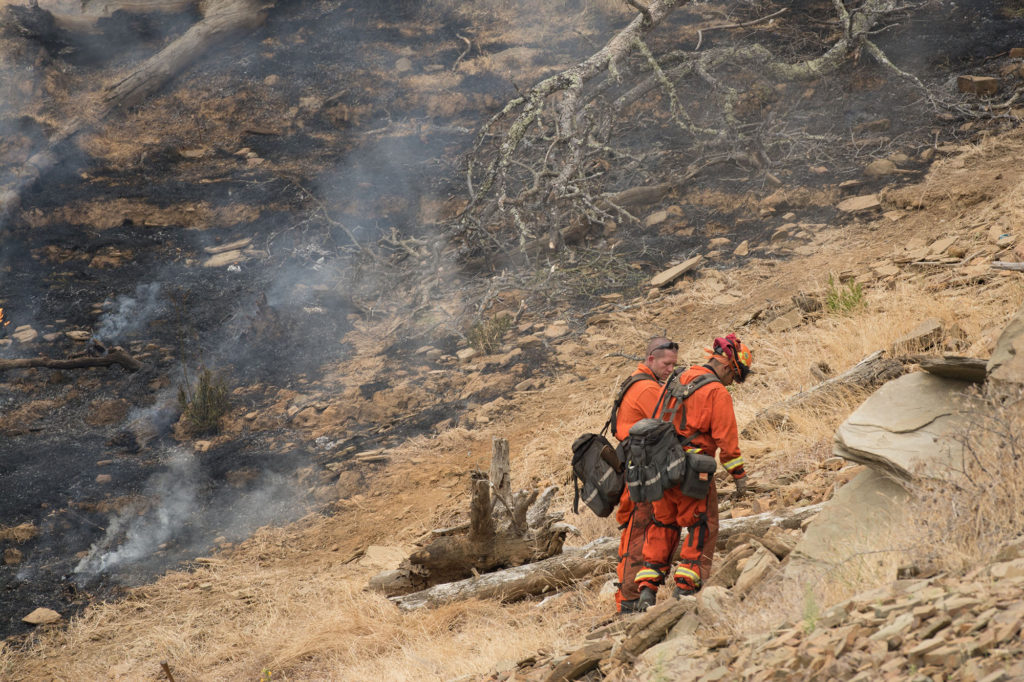

Both temperate grasslands and tropical savanna are susceptible to fires. Dry conditions combined with the fuel of dry leaves can lead to fast-burning fires.
Fires kill grass pests and also speed up recycling of nutrients back to producers.
Intermountain grasslands, like those found in California can be particularly susceptible to grassland fires as the grasses dry out in the summer and fires are flamed by high and dry fall winds.


Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
list characteristics of grass plants?
-
describe the climate characteristics of temperate grasslands, and provide examples in different parts of the world?
-
describe the climate characteristics of tropical savannas, and the role of fire in grassland ecosystems?