Biome Patterns Repetitive Occurrences in Nature


Biome Patterns Outcomes
-
Describe light and the colors we see and how they relate to leaf colors in various habitats.
-
Provide characteristics of water and plant responses to water availability.
-
Describe how plants are impacted by, and respond to, wind and extreme temperatures.
-
Describe the rainshadow effect.
-
Provide the locations of two large rainshadows in Oregon.
-
Describe changes in vegetation as you head west to east across Oregon.
Light & Color
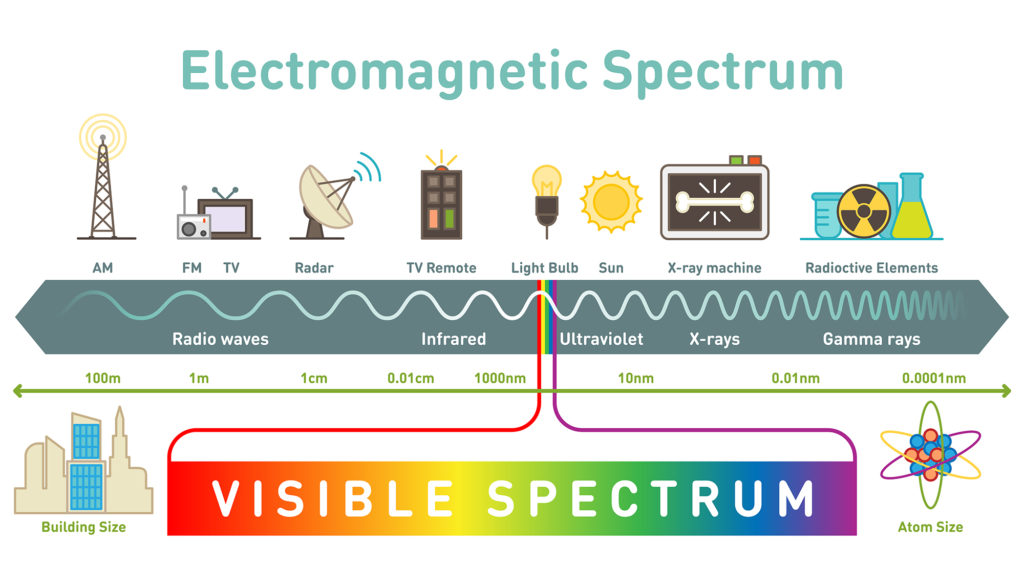
When white light passes through a glass prism, we see a rainbow of colors with visible (to humans) wavelengths.

The color we see is reflected off, not absorbed by, an object. If we see a green leaf, the green wavelengths were reflected off of the plant.
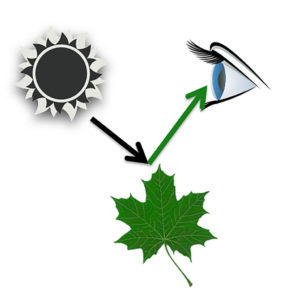

When you see a spinach leaf, the green color comes from the dominant green chlorophyll pigments, but other color pigments are present.
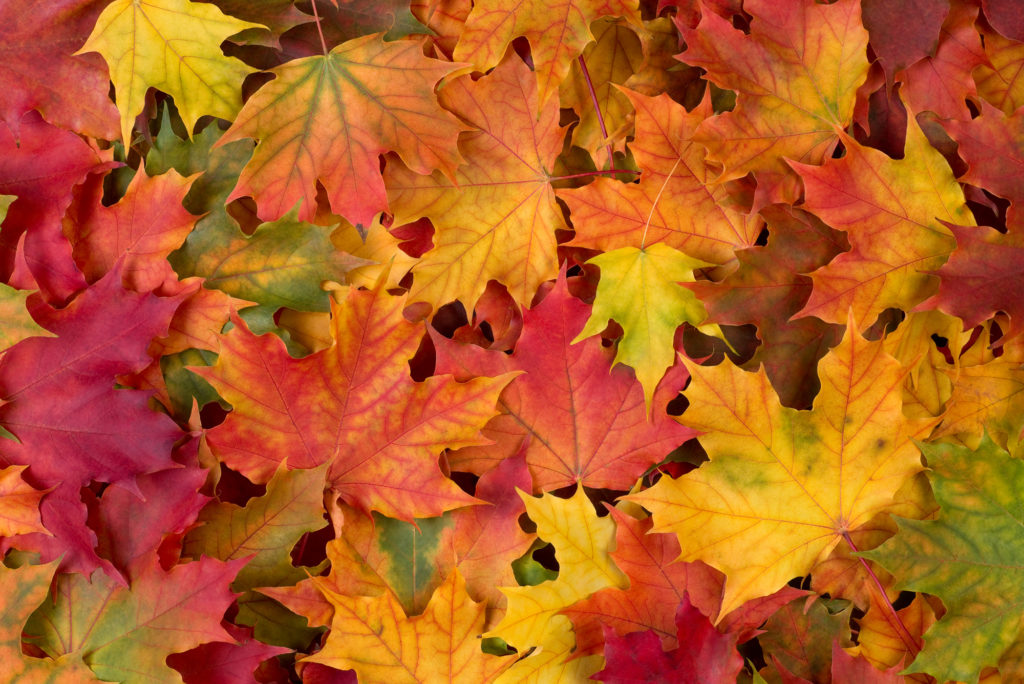
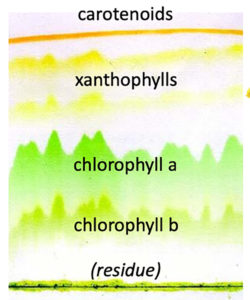

Fall leaf colors occur when chlorophyll degrades as winter approaches, day length shortens, and temperatures cool. Loss of chlorophyll reveals yellow, orange, and red pigments (carotenoids and xanthophylls) that were always there, but in lesser amounts than the green chlorophylls.

Producers high in Carotenoids

Consumers who eat them
Leaf color can relate to light intensity.

High Light

Low Light
Water
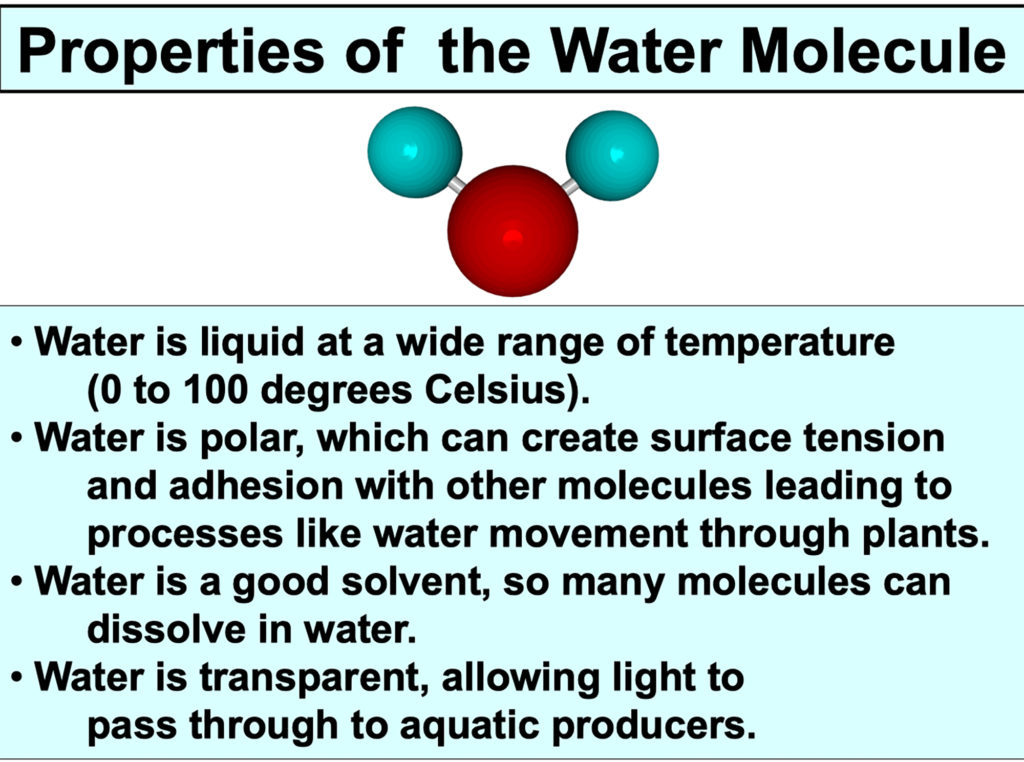
Water cover approximately 71% of the Earth\’s surface and is found in all organisms. The molecule has a group of properties that make it well-suited for supporting life as we know it.
Water can also have a negative impact on organisms. Water indirectly impact plants by eroding away the soil.


Sometimes you can find a ribbon of trees within a larger grassland. That indicates water is present, possibly a stream or highway with ditches alongside.
Succulent (water storing) plants that live in desert habitats have a variety of structural features that reduce water loss.

Wind & Temperature
Wind can have a significant impact on species.

Wind can increase water loss, erode at plant structures, and drop temperature barriers around a plant.
Wind can also increase rates of soil erosion.


Plants in windy habitats have structural features that reduce exposure.
These are similar to adaptations plants have in cold habitats.

Conifer needles and cactus needles are both examples of leaf shapes that reduce exposure to harsh environmental conditions, including extremes in temperature.

Pines that have evolved in windy coastal environments over time have a different growth form than pines living on central mountains.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
describe light and the colors we see and how they relate to leaf colors in various habitats?
-
provide characteristics of water and plant responses to water availability?
-
describe how plants are impacted by, and respond to, wind and extreme temperatures?

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
describe light and the colors we see and how they relate to leaf colors in various habitats?
-
provide characteristics of water and plant responses to water availability?
-
describe how plants are impacted by, and respond to, wind and extreme temperatures?

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
describe light and the colors we see and how they relate to leaf colors in various habitats?
-
provide characteristics of water and plant responses to water availability?
-
describe how plants are impacted by, and respond to, wind and extreme temperatures?

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
describe light and the colors we see and how they relate to leaf colors in various habitats?
-
provide characteristics of water and plant responses to water availability?
-
describe how plants are impacted by, and respond to, wind and extreme temperatures?

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
describe light and the colors we see and how they relate to leaf colors in various habitats?
-
provide characteristics of water and plant responses to water availability?
-
describe how plants are impacted by, and respond to, wind and extreme temperatures?

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
describe light and the colors we see and how they relate to leaf colors in various habitats?
-
provide characteristics of water and plant responses to water availability?
-
describe how plants are impacted by, and respond to, wind and extreme temperatures?