Community Interactions Between Different Species


Community Outcomes
-
List positive, negative, and neutral forms of community interactions, including specific examples of predators, herbivores, and types of competition.
-
Describe what scavengers, detritivores, and decomposers consume, including why they are significant to other species.
-
Provide examples of carnivorous plants, including how they catch their prey.
There are many types of interactions between species within a community. The impacts on individual organisms can be positive, negative, or neutral.
Community Interactions

Predation

Herbivory

Parasitism

Competition

Mutualism

Commensalism
Parasitism, Mutualism, and Commensalism are all examples of symbiosis: living in close association over time. These interactions are described in more detail on the Symbiosis page.
Here we\’ll examine examples of predation, herbivory, and competition.
Predation
Predators have structures and behaviors that assist is catching prey. This crocodile has a variety of advantages: camouflage, stealthy movement, speed, strength, and weaponry.
You can imagine how a prey animal may not even see it coming.
Piranhas form large schools in South American rivers and can kill prey fish with their powerful jaws and sharp teeth.
Watch this classic predator move: turning its back on the camera.
Preying mantises (also called praying mantises) use a variety of techniques to capture their prey.
Our native mantises have green camouflage color and are shaped like grass blades. They are hard to see even when you are looking for them.
Ghost preying mantises look like dry leaves and sway back and forth like a leaf in the breeze as they move in on their prey. This species will grow to about four inches in size

Prey are not defenseless. They can run, fly, maneuver, fight back, freeze, hide, or a combination of these.
If you have ever tried to pick up an unwilling rabbit, you know they can kick, bite, and injure a potential predator.
Herbivory

Herbivory is consumption of producers, typically plants or algae. There are many specific types of herbivores, including:
-
Grazers: Eat a variety of plant leaves, like grasses, that are close to the ground
-
Browsers: Eat a variety of plant parts, including leaves, branches, and fruits
-
Algivores: eat algae
Identify these three herbivores as eating as a grazer, browser, or algivore.



Competition
Competition occurs when organisms are trying to utilize the same limited resources.

Intraspecific Competition

Interspecific Competition
These crickets and sowbugs are competing for the same food.
Is this intraspecific or interspecfic competition?
Interactions can also occur between a living organism and one that has already died.

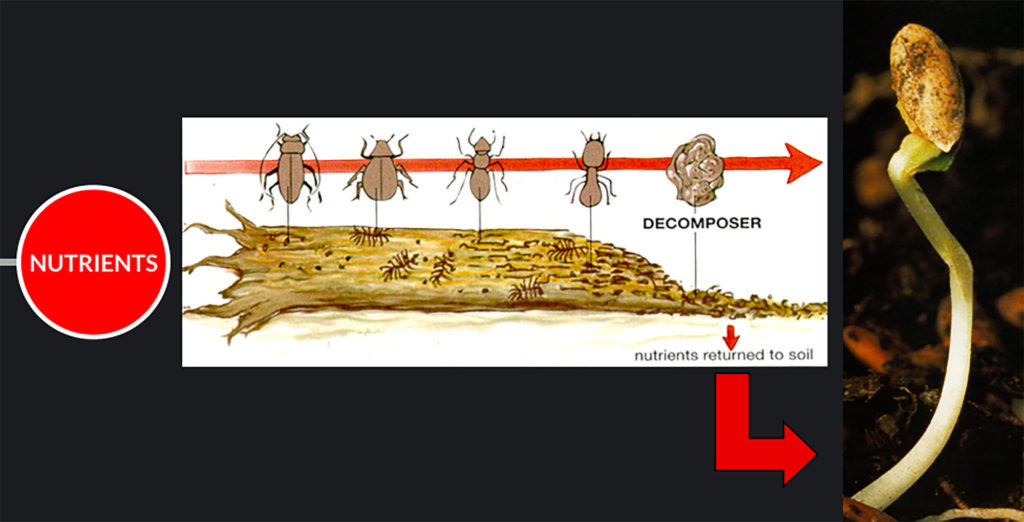
Scavengers break down a recently dead organism (a corpse) into smaller pieces called detritus.
Detritivores eat small recently dead organisms and pieces of detritus from larger organisms.
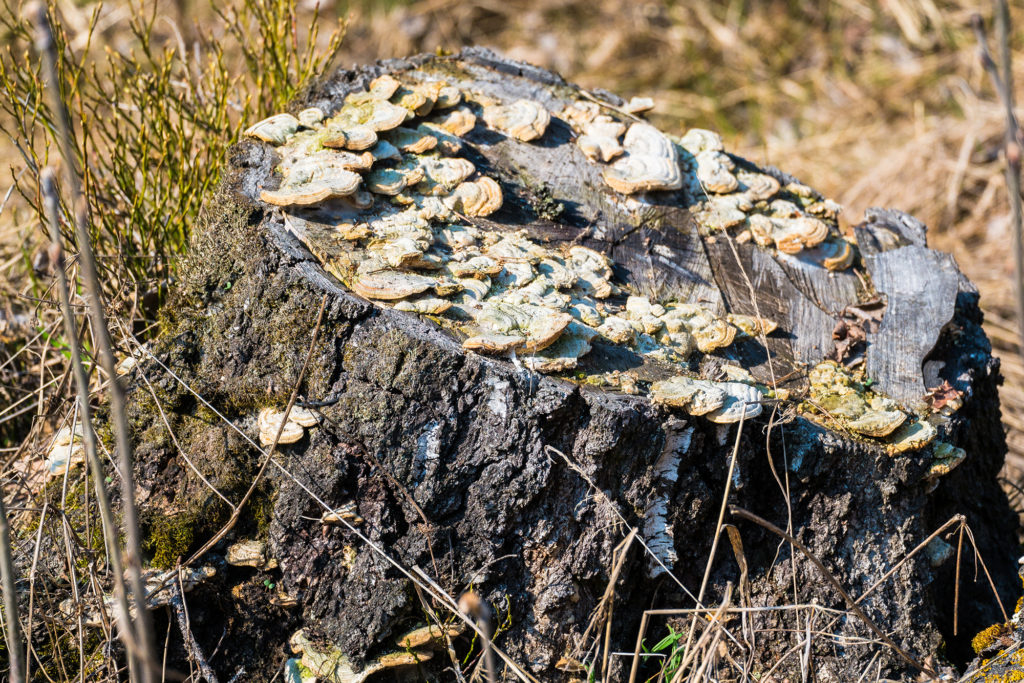
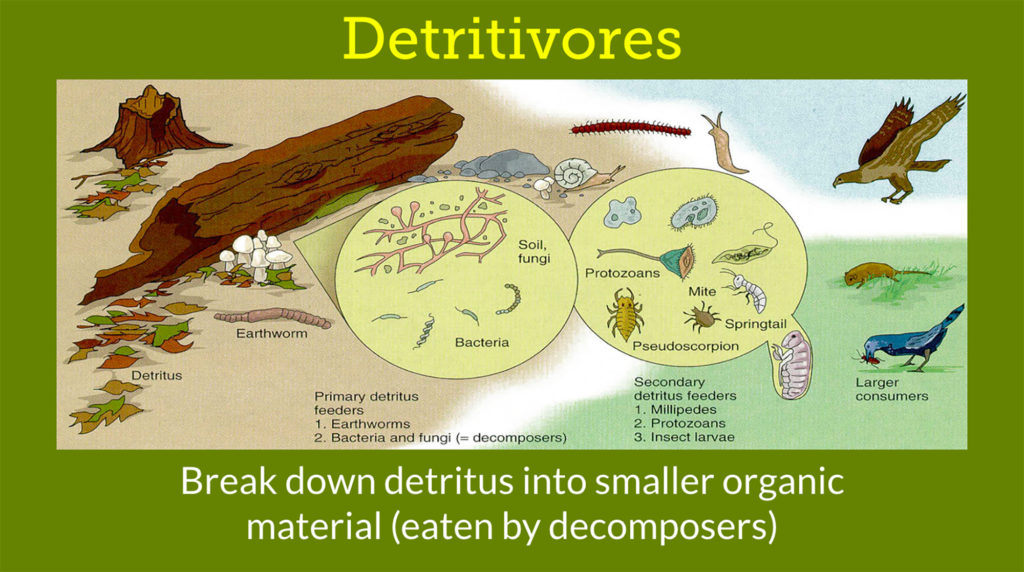

Decomposers, including fungi and some species of bacteria, break organic matter into small molecular form, enabling nutrients to recycle back to the producers.
A Special Case: Carnivorous Plants
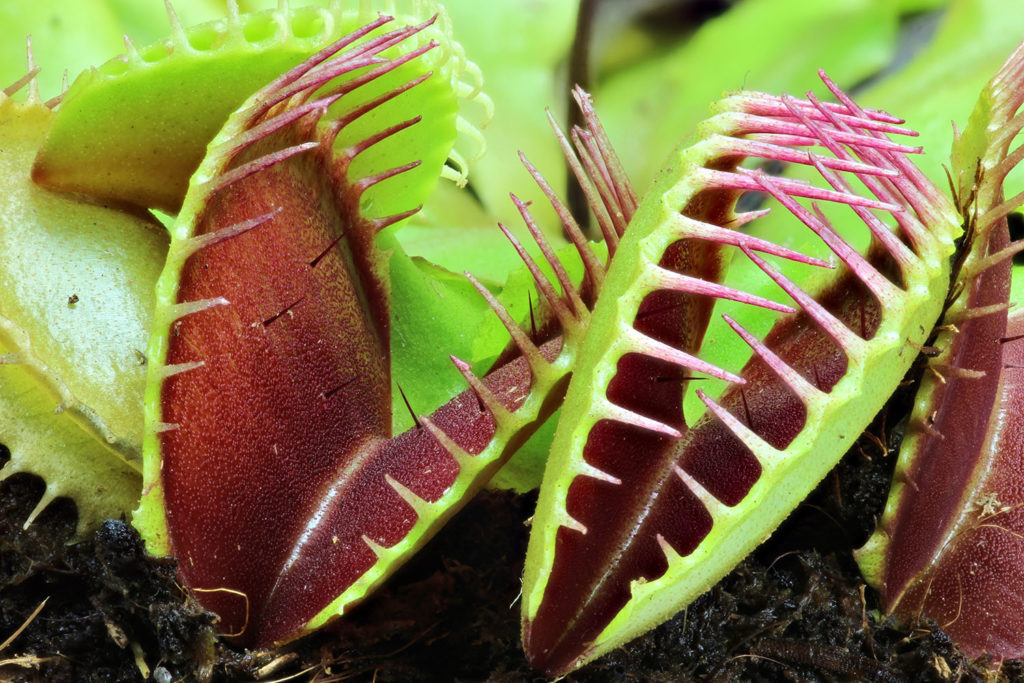

Carnivorous plants can acquire nutrients through their roots and photosynthesize with their leaves, but they can also supplement their diet by capturing prey.
These plants are often found in nutrient-poor soils where decomposition is slow, like an acidic bog.
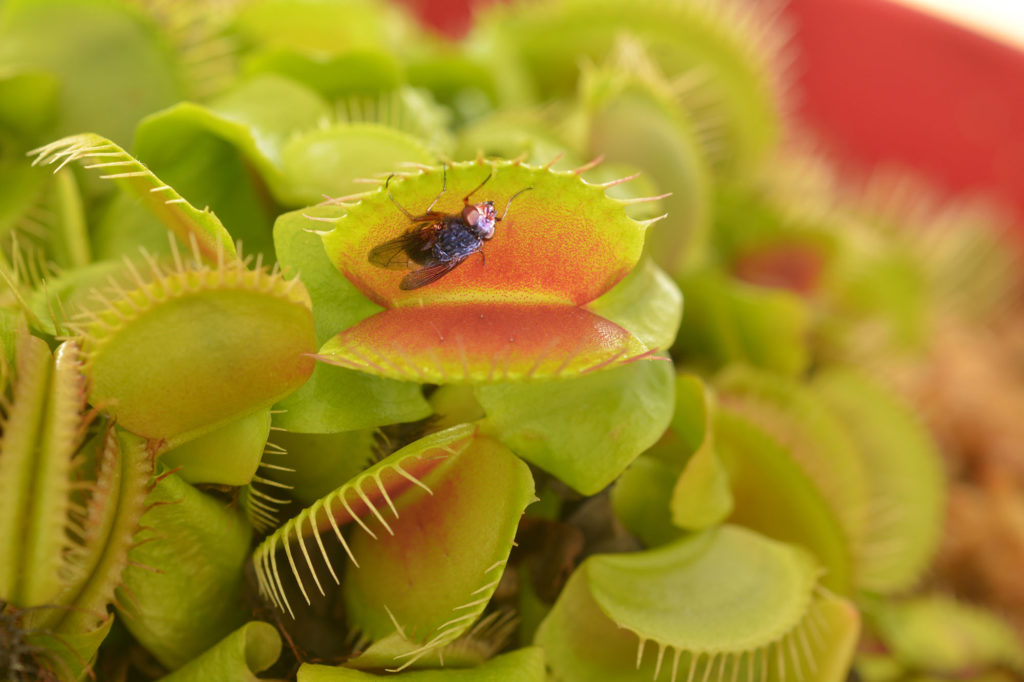

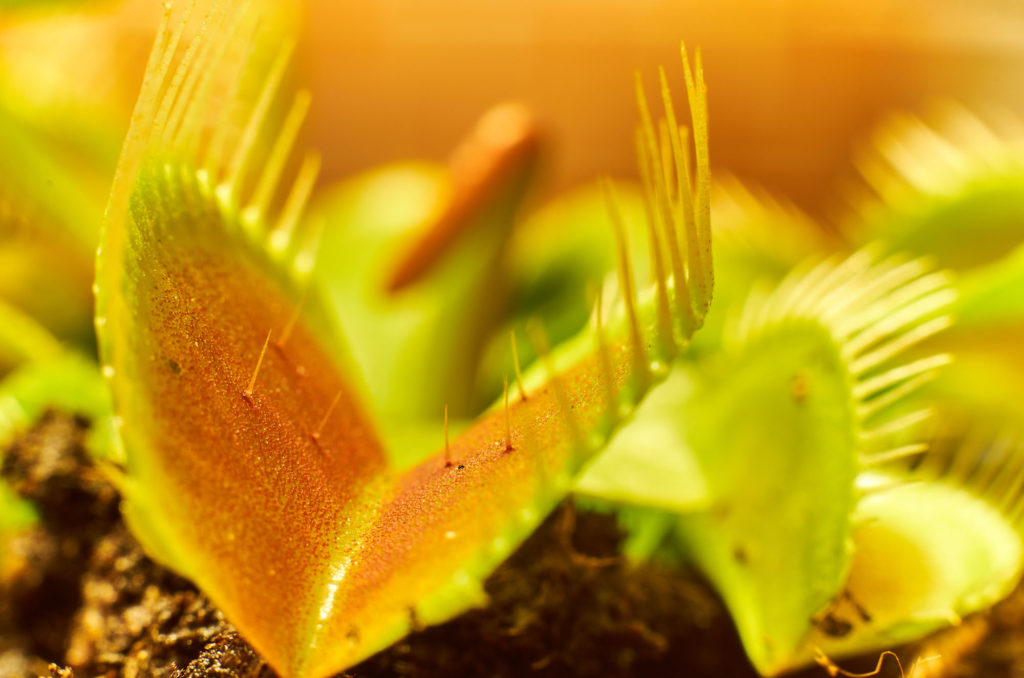
Leaves are modified as traps. The leaves of Venus Fly Trap (Dionea sp.) have tiny trichomes (hairs) that trigger the leaf to snap closed, trapping the prey.

Sundew plants have small hairs (trichomes) that are covered in a sticky substance that trap insects.

Pitcher plants have leaves shaped like cups. Trichomes lead the prey to the water where they drown and are digested by enzymes.


Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
list positive, negative, and neutral forms of community interactions, including specific examples of predators, herbivores, and types of competition?
-
describe what scavengers, detritivores, and decomposers consume, including why they are significant to other species?
-
provide examples of carnivorous plants, including how they catch their prey?