Flowers Reproductive plant structures

The Flowers activity meets for 50 minutes the first week (welcome week 0). That will be Thursday or Friday in room 127 or 129 Weniger, depending on your course schedule.

Flowers Outcomes
-
Identify flower structures and functions, relating flower structures to fruits and seeds.
-
Describe the characteristics of flowers that attract specific pollinators, and explain how CCD may be significant to bee-pollinated flowering plants.
-
Describe the flowers of wind-pollinated plants.
This video provides an overview of flowers.
Let\’s start with basic flower structure.
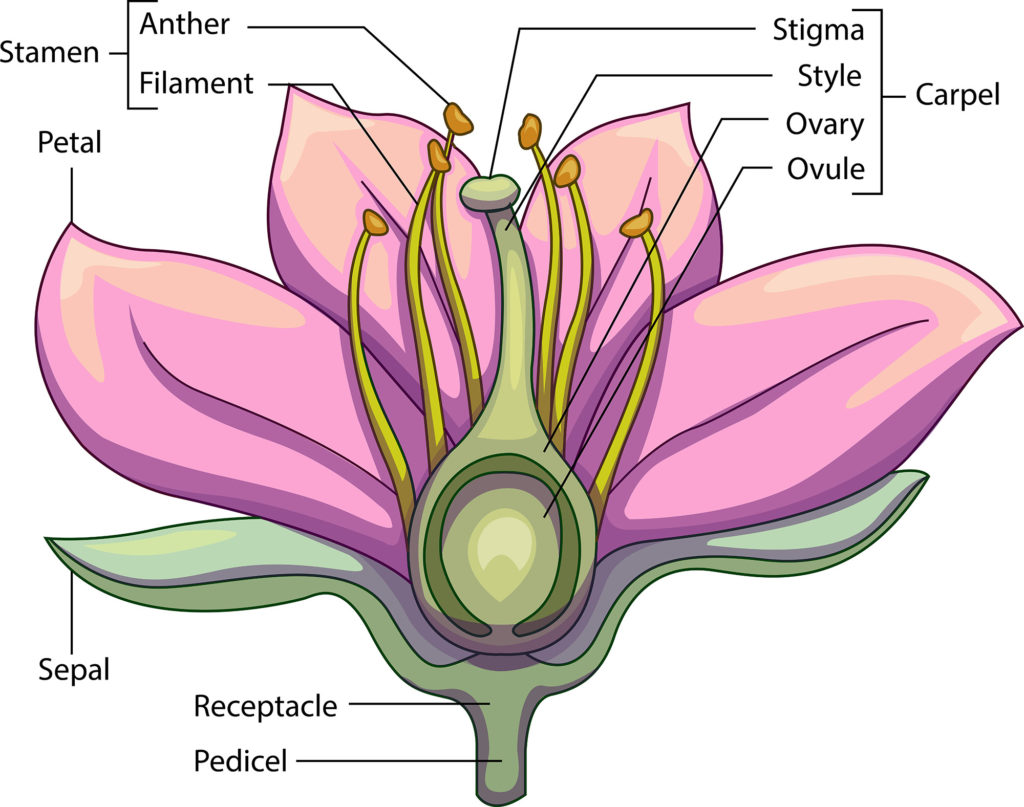
Stamens are the \”male\” reproductive structures of the flower that produce the pollen grains. Each stamen consists of a filament and an anther. The filament is a stalk attached to the anther. The anther is where pollen grains are located. Pollen is the equivalent to sperm in human males.
The pistil (also called the carpel) is the \”female\” reproductive structure of the flower and is made up of three parts. The stigma is where the pollen grains land. The style is below the stigma and connects it to the ovary. The ovary forms the bottom part of the pistil. Inside the ovary are the ovules and inside the ovules are the eggs which, after fertilization, will result in the ovules developing into seeds. At the same time the ovary will develop into a fruit.
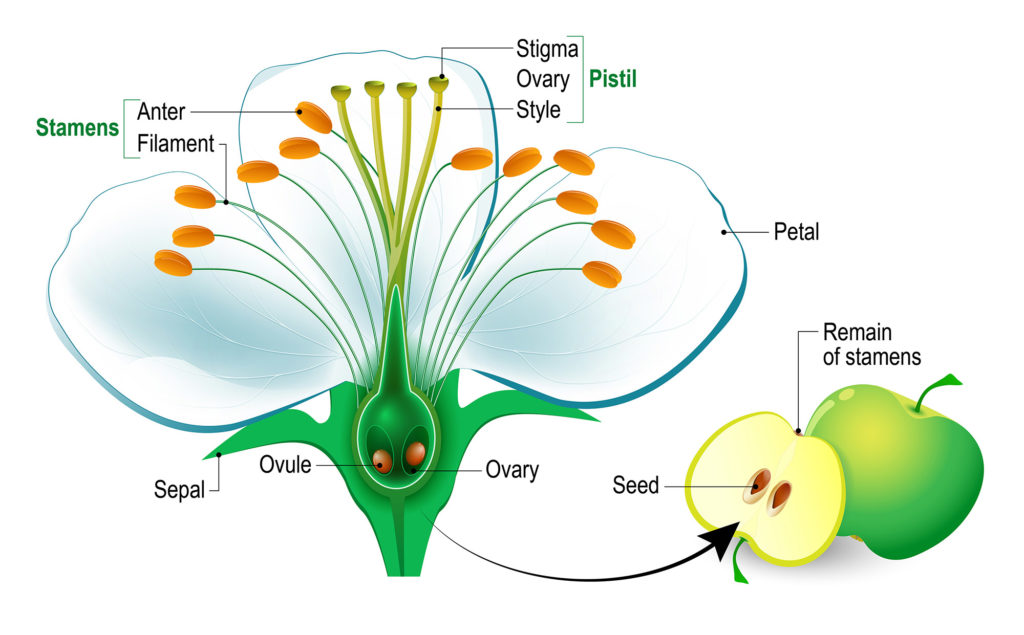
Flowers have varied arrangements of the stigma and stamens. This flower has a branched stigma that can accept pollen and stamens lined up on the outside of the style.
To review; after fertilization (pollination), the ovary of the flower becomes the _____ and the ovules become the _____.
Answers: fruit; seeds
Pollinators are often attracted to flowers with specific colors, patterns, odors, or sizes/shapes.
Pollinator Preferences

Bees

Flies

Butterflies

Night-Feeding Moths

Bats

Beetles

Hummingbirds
Anything Goes
Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD)
In recent years, worker bees have been found dead in piles near the entrance to hives. The cause of CCD may be complex, a combination of factors that include pesticides, disease, climate change, and reduced food availability.
Since bees pollinate significant crops, including beans and fruit trees, losses of bees can have a significant economic impact and even reduce food supply.
Although many significant crops like soybeans and squash are pollinated by animals, grass plants are wind pollinated. Grasses include corn, wheat and rice.
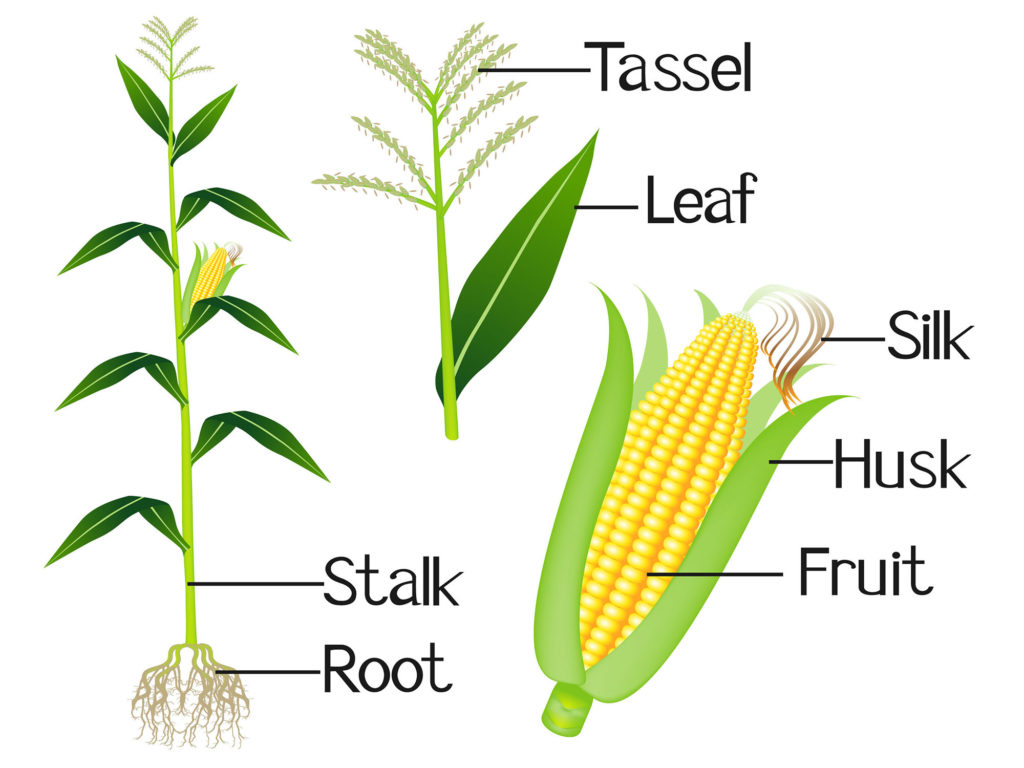
In a corn plant, a cluster of male flowers is called a tassel. The male flowers produce pollen which is carried by the wind to female flowers. Pollen falls onto the silks of female flowers, which develop into individual corn kernels. Typically the male and female flowers on a single plant mature at different times, to prevent self-pollination.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
identify flower structures and functions, relating flower structures to fruits and seeds?
-
describe the characteristics of flowers that attract specific pollinators, and explain how CCD may be significant to bee-pollinated flowering plants?
-
describe the flowers of wind-pollinated plants?