Soils Complex underground food webs


Soils Outcomes
-
Describe the typical components and characteristics of topsoils.
-
Provide examples of organisms commonly found in soil food webs.
-
Explain the classification, basic structures, and functions of soil bacteria and fungi.
This video introduces topsoil.
Topsoil, the soil that we come in direct contact with, is comprised of three components: minerals, organic matter (the remains of organisms), and living soil organisms.
Soil organisms are critical in breaking the remains of other organisms into nutrients that can reenter the food web.
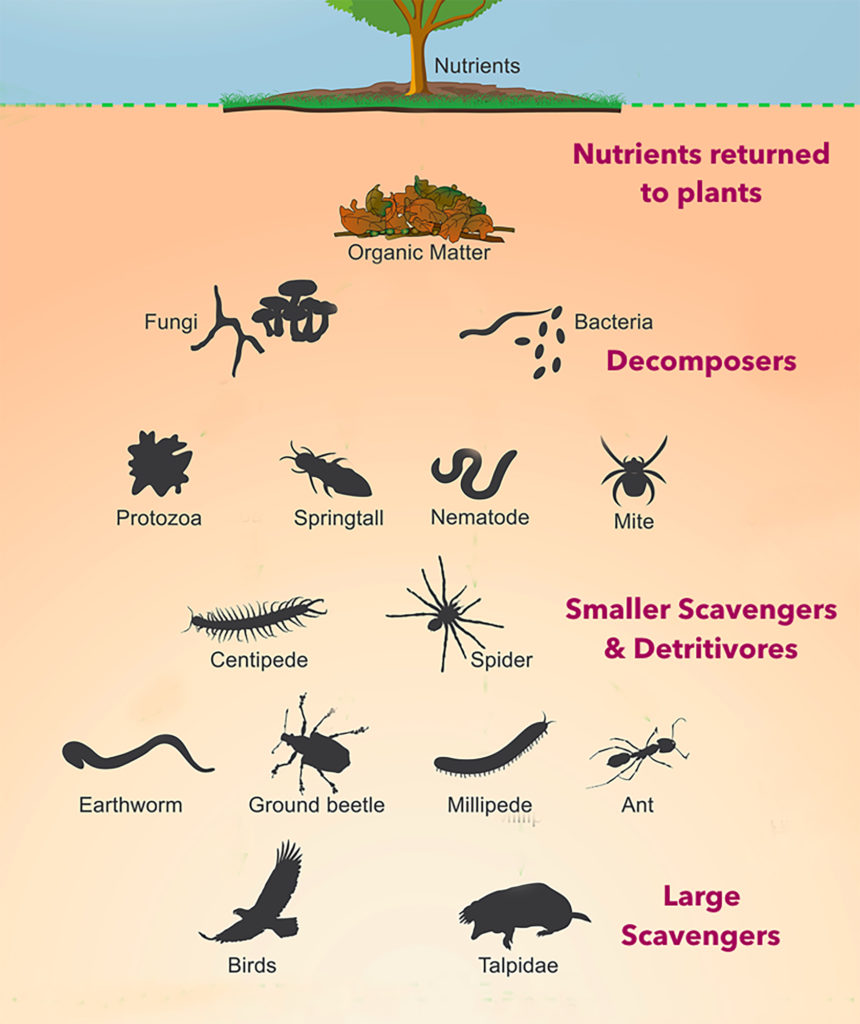
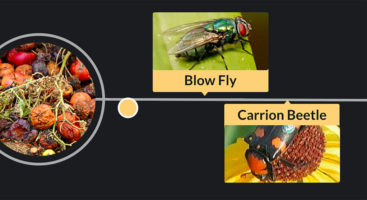
From last week\’s lecture, what do we call the organisms that directly eat corpses, scat, or leaves, breaking them down into detritus?
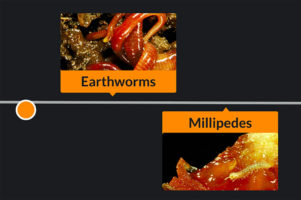
What do we call the organisms that consume detritus, breaking it down into organic matter?
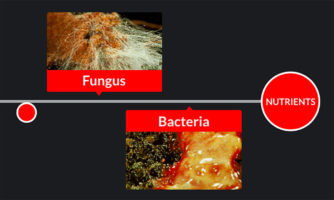
Fungi and some bacterial species are _____ that can break the organic matter down into nutrient form, that can be reutilized by producers.
These dermestid beetles and their larvae scavenge (consume) dead organisms.
Note: beetle larvae are consuming an animal corpse

From earlier in this course, taxonomic classification is naming organisms based on their structures like bones and teeth, and more recently their genetic structures as well.
Organisms are classified in one of three Domains. The Domains are Eukaryota, Bacteria, and ________.
Functional classification, based on what an organism does in a community, includes the producers, _____, and decomposers.
Sowbugs are taxonomically classified in Domain _____ and functionally classified as _____.
Fungi can also play a key role in soil food webs. From last week\’s lecture, answer these questions.
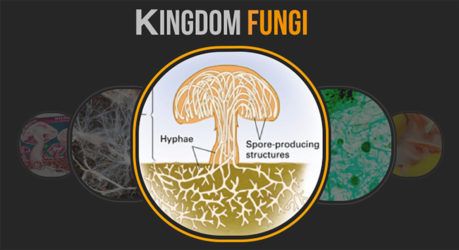
The mushrooms we see above ground are the structures some species of fungi use for _____.

The hair-like structures that make up the body (mycelium) of a fungus are called _____.

Fungal hyphae secrete _____ to break down the materials they are digesting.
Bacteria are significantly different that fungi, but some species of bacteria are also decomposers.
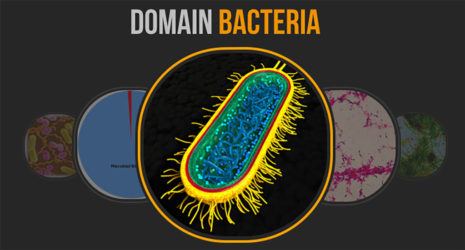
A bacterium (individual bacteria) is made up of only _____ cell.
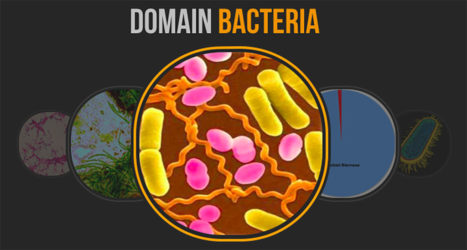
Bacteria generally have three basic shapes. What are they?

What is the group of bacteria we have met that photosynthesize and can be found in lichens and Azolla ferns?

Mycorrhizae
The relationship between the fungus and the plant root it live inside is most likely _____.

Rhizobium
The relationship between the bacteria and the plant root it lives inside of is most likely _____.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
describe the typical components and characteristics of topsoils?
-
provide examples of organisms commonly found in soil food webs?
-
explain the classification, basic structures, and functions of soil bacteria and fungi?