
Brain Emotion, Memory, & Learning

Brain Objectives
-
List different brain structures and their functions as well as the characteristics of brain disorders.
- Explain how neurotransmitters relate to emotions and how neurotransmitters can relate to depression.
-
Describe what forms when you make a memory, and the role of learning strategies, nutrition, and sleep.
When you ask someone what is special structurally about humans compared to other animals, the answer is often “our brains.” We share similar brain structures to other species alive on Earth today, particularly other primates, but there are characteristics that are well-developed in the human brain.
For example, you can recognize that the brain in the photo is not a real brain, but a model of a brain. You can recognize that an object is not the “real thing” and realize it is a representation of reality. This is just one of several abilities made possible by the structure of our brains.
This video introduces basic brain structure and the interactions between brain cells.
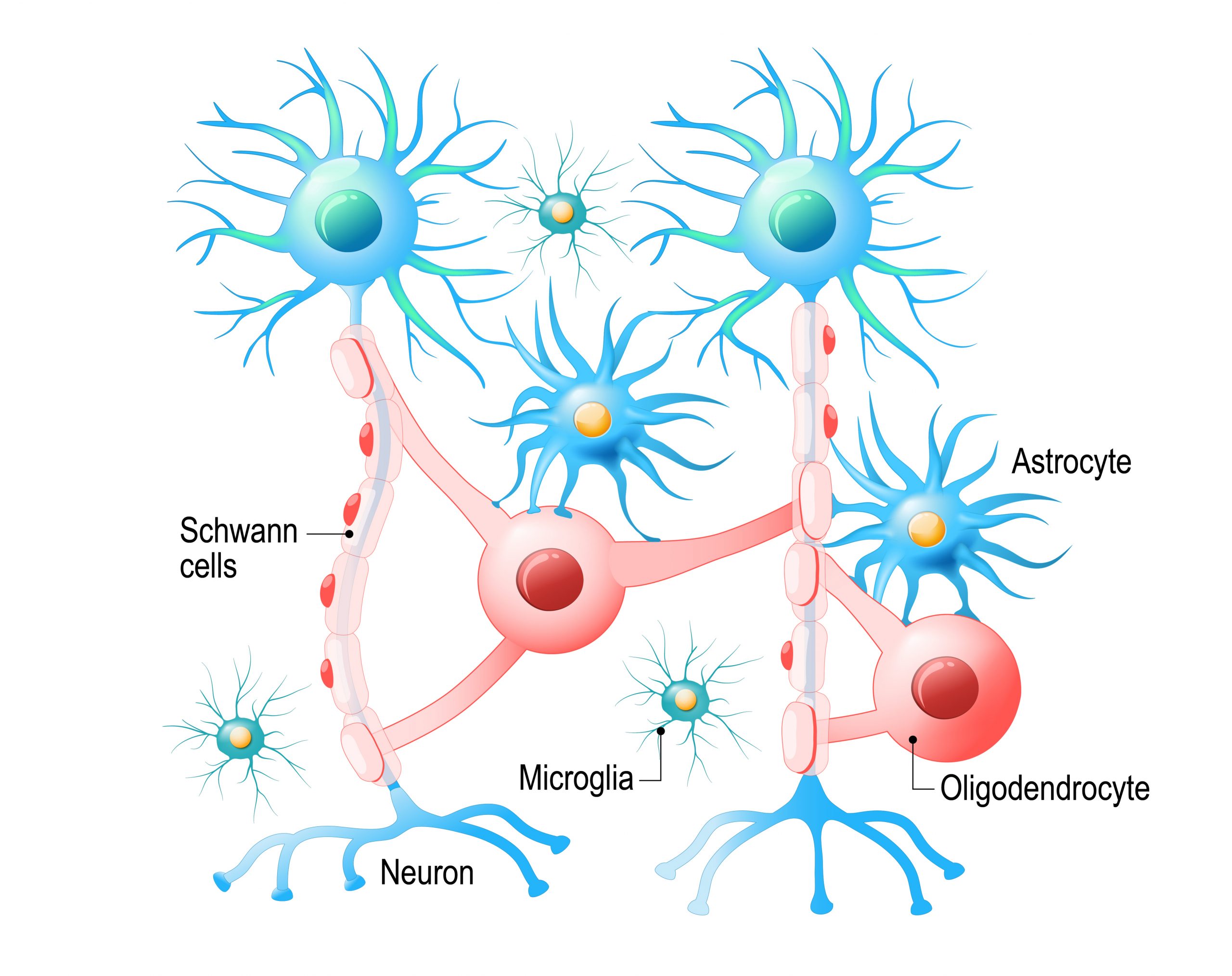
The brain is more than just neurons. _____ cells support the neurons, keeping them fed, protected, and anchored in place.
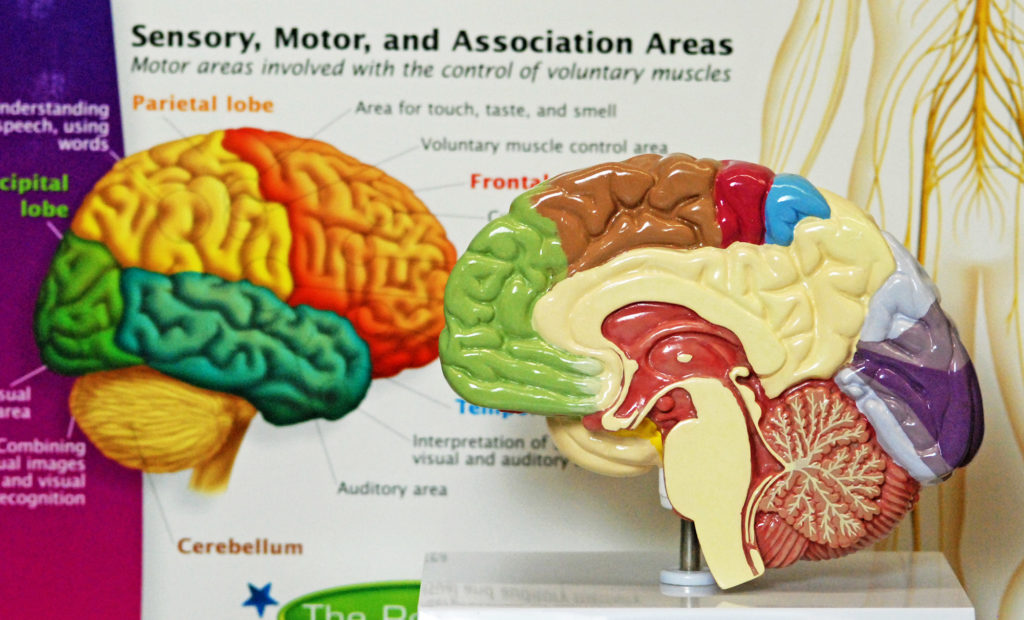
The brain is more than the massive folds of cerebral cortex, also called the “cerebrum.”
This video shows a few of the other brain structures.
We have voluntary somatic motor control of many body parts. This video shows the parts of the parietal lobe of the cerebral cortex involved in receiving sensory information and outputting voluntary motor control.
There are many brain disorders. This video introduces a few that may be familiar. We will have additional brain disorders in the next guide on aging.
Neurons of the cerebral cortex
Emotions
Neural synapses play a role in emotions, especially the neurotransmitters that signal the next neuron. This video provides a context for understanding the biological basis of emotions.
Emotions are impacted by both external and internal factors. The impact of external factors varies widely from person to person. A piece of art can elicit warm feelings of happiness in one person, sorrowful memories in another, or no emotional response at all.
Chronic (long-term) stress can alter blood flow and impact neurotransmitters.
Memory
At the most basic level, a memory is formed when neurons synaptically connect together. This video introduces the process of making memories.
Memory has two components: memory formation and memory recall. Games are sometimes used to strengthen both of these processes.
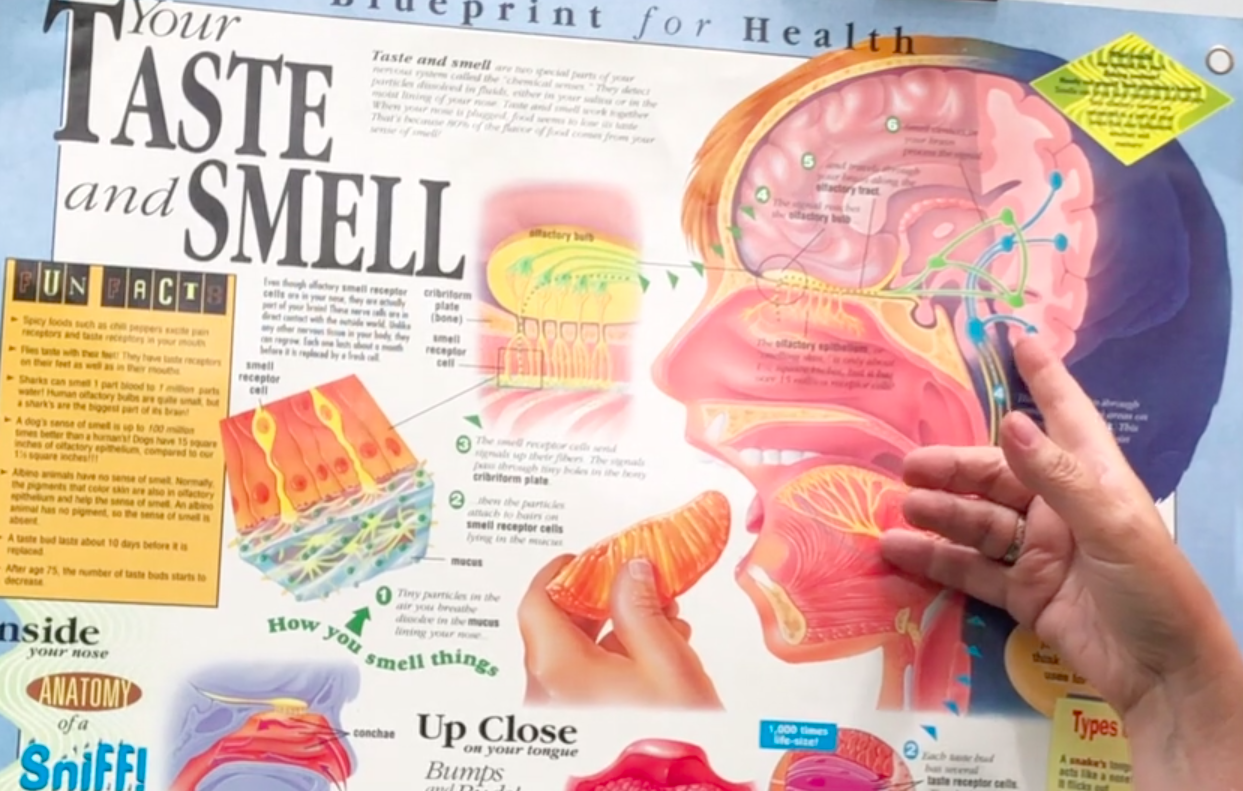
Some sensory experiences like certain scents and tastes can form a strong memory. It could be a familiar family dish, or a loved one’s perfume. Scent, taste, and memory centers in the brain overlap, including in portions of the thalamus and frontal lobe.
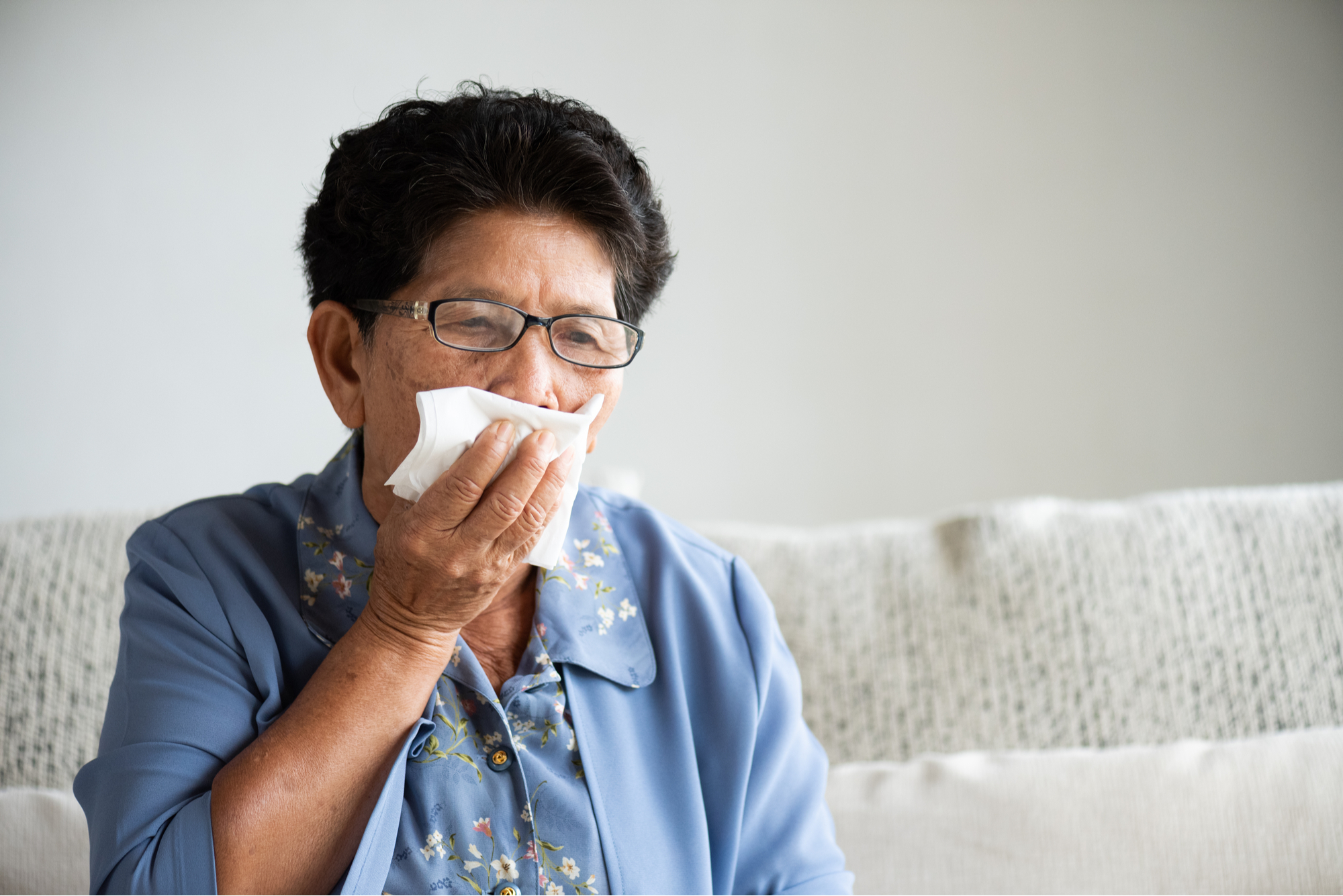
If you have a cold or allergies and temporarily lose your sense of smell, you may also have difficulty tasting food. The neural interpretation of scents and tastes are often synaptically connected and with incomplete olfactory input, the brain can find it challenging to recognize a taste.

Hands off my doughnuts!
In some cases it is possible to purposely form new memories in order to alter behaviors and emotional responses.
Note: you may associate doughnuts and fish after watching this video.
Four factors can increase the likelihood of learning:
Goal Insight: Knowing what the task is and what successful completion looks like.
Repetition: Trying something over and over until you figure out the most successful process.
Trial & Error: Being willing to make mistakes and learning from mistakes to improve performance.
Reduction of Interferences: Finding and eliminating possible distractions that may interfere with learning.
Determine the impact of goal insight, repetition, trial & error, and reduction of interferences on successful completion of this finger maze. You will be discussing these in the next journal assignment.
Start your first journal assignment here
Journal Page #9: Learning Strategies
Describe how you can use each of these four strategies to positively impact your own learning:
- Goal Insight
- Repetition
- Trial & Error
- Reduction of interferences

You are turning in a thorough description for how you can utilize each of the four learning strategies (goal insight, repetition, trial & errror, reduction of interferences) to improve your own learning.
You may want to contextualize this on how you are approaching remote learning instead of utilizing traditional campus study spaces and routines.
The next section explores the amazing capabilities of the human senses.
Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
list different brain structures and their functions as well as the characteristics of brain disorders?
- explain how neurotransmitters relate to emotions and how neurotransmitters can relate to depression?
-
describe what forms when you make a memory, and the role of learning strategies, nutrition, and sleep?



