
Nervous System Communication & Coordination


Nervous System Objectives
-
List the organs and functions of the central and peripheral parts of the nervous system, including the locations of the sciatic nerves, median & ulnar nerves, and cranial nerves.
-
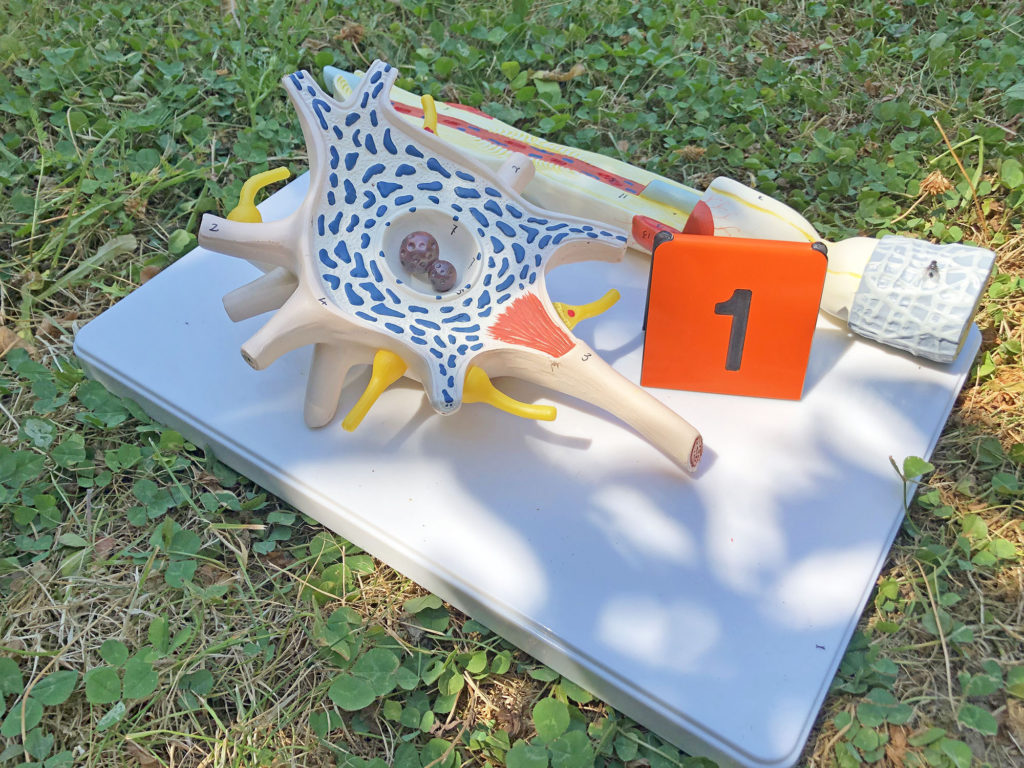
Identify the parts of a neuron in a drawing or microscopic image, including the dendrites, cell body, axon, and myelin.
-
Explain what occurs at a synapse when one neuron communicates with another neuron.

The nervous system not only keeps us breathing and circulating blood, it also can solve complex problems like a Rubik’s cube.
We are starting our examination of the nervous system with two brief and complementary overview videos.
Nerves are bundles of neurons (nerve cells) that (1) receive sensory information, (2) send it to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) for processing, and then (3) respond in some motor fashion, like causing muscle to contract.
The motor nerve response is voluntary and under our control is called _____, are the nerve response that is involuntary and out of our control is called _____.

The autonomic (sometimes called “vegetative”) part of the motor nervous system has two components that generally work opposite each other: the _____ that often stimulates organ activity, and the _____ that often inhibits organ activity.
The nerves are often running along large blood vessels throughout the body.
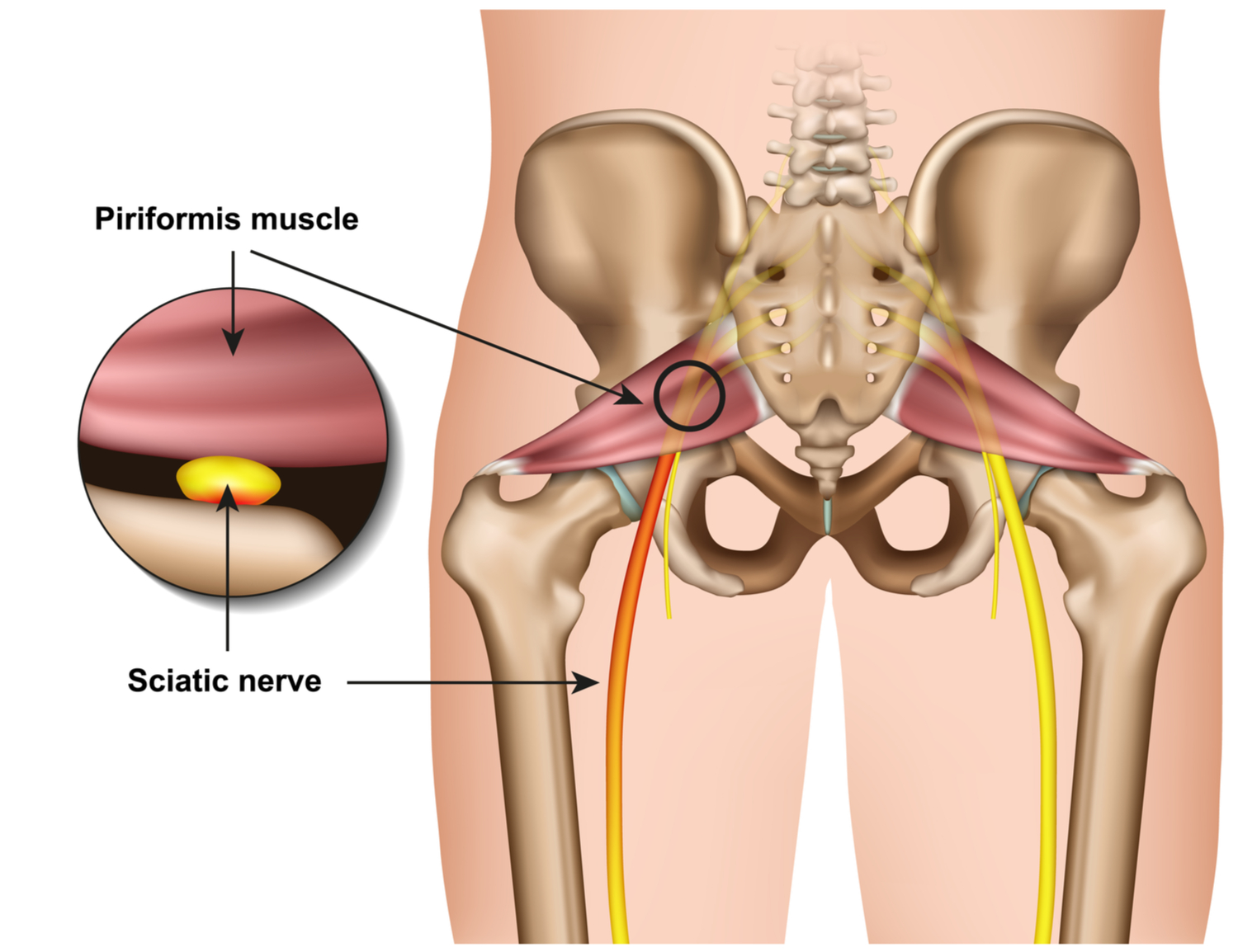
Sciatic Nerves
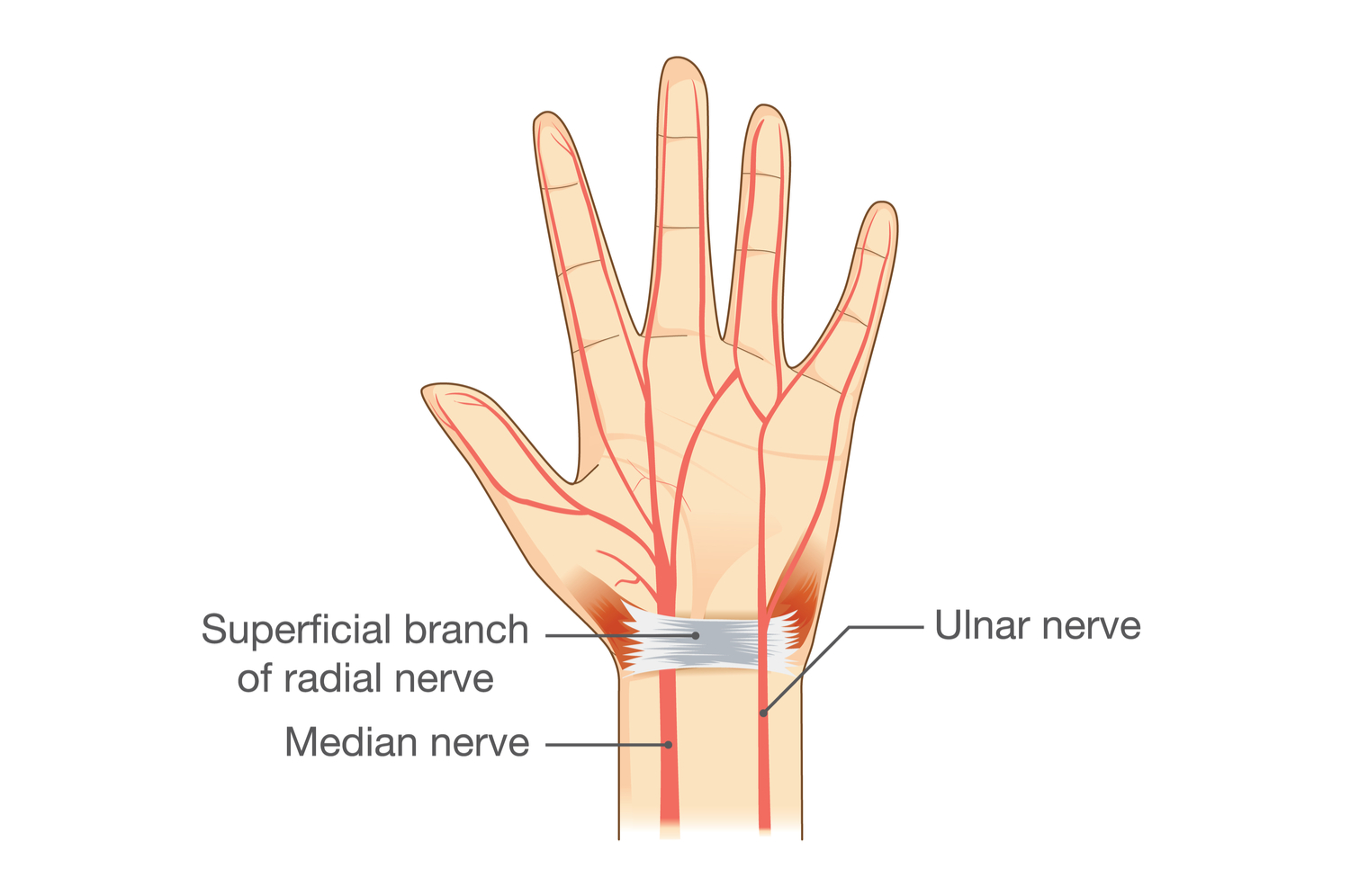
Median and Ulnar Nerves
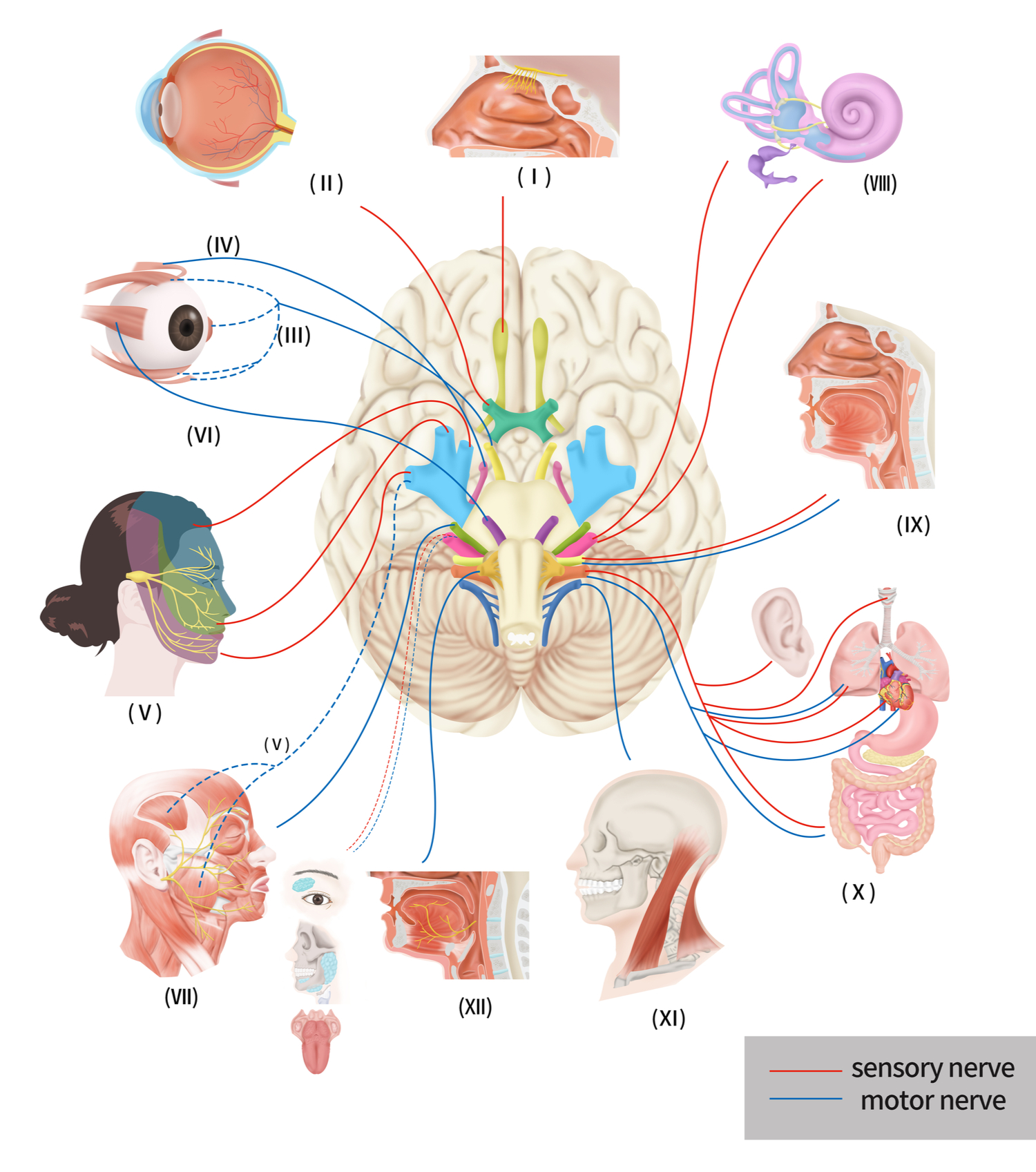
Cranial Nerves
Neurons
Next we are examining neurons, the cells that connect together and communicate.
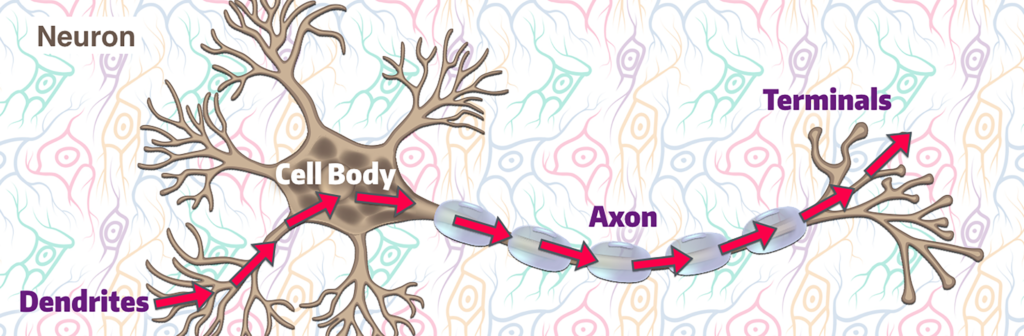
Neurons are the connected cells that communicate information rapidly around the body. Signals enter the ___, travel through the ___ ___, down the long ___, and out the ___ ___.
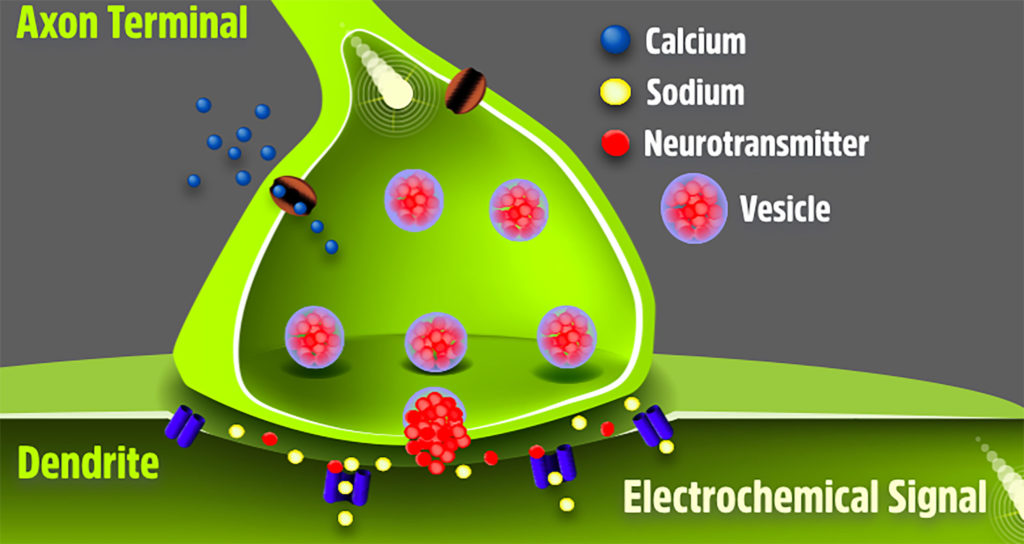
Neurons connect together at the synapse, where the axon terminal of one neuron contacts the dendrite of the next neuron. Movement of calcium causes neurotransmitters to spill into the gap between neurons, and causes sodium to move into the next neuron.
This is another example of why calcium and sodium are important to organ function.
In this model of a synapse, identify the axon terminal with a mitochondrion, vesicles of neurotransmitters, small dots representing calcium and sodium, and the next neuron’s dendrite.
Fat plays a role in nervous system function. Why is myelin important?
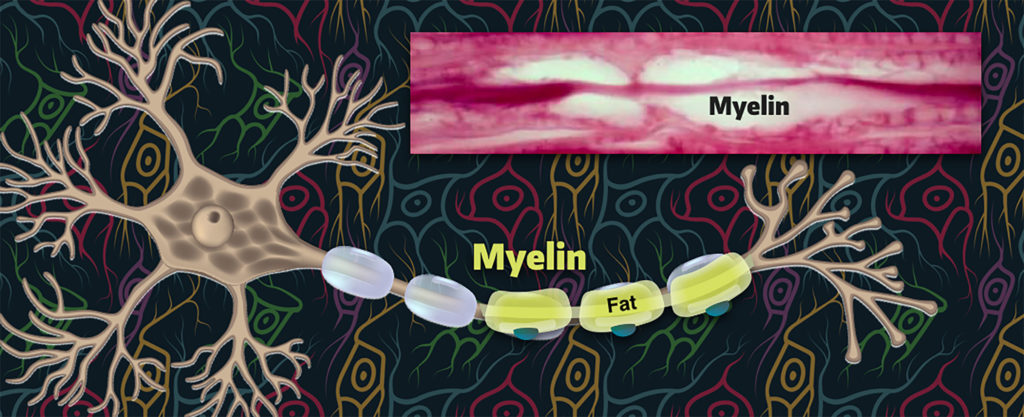
The glial cells that wrap around a neuron’s axon are called Schwann cells and they produce layers of myelin that insulates the axon.
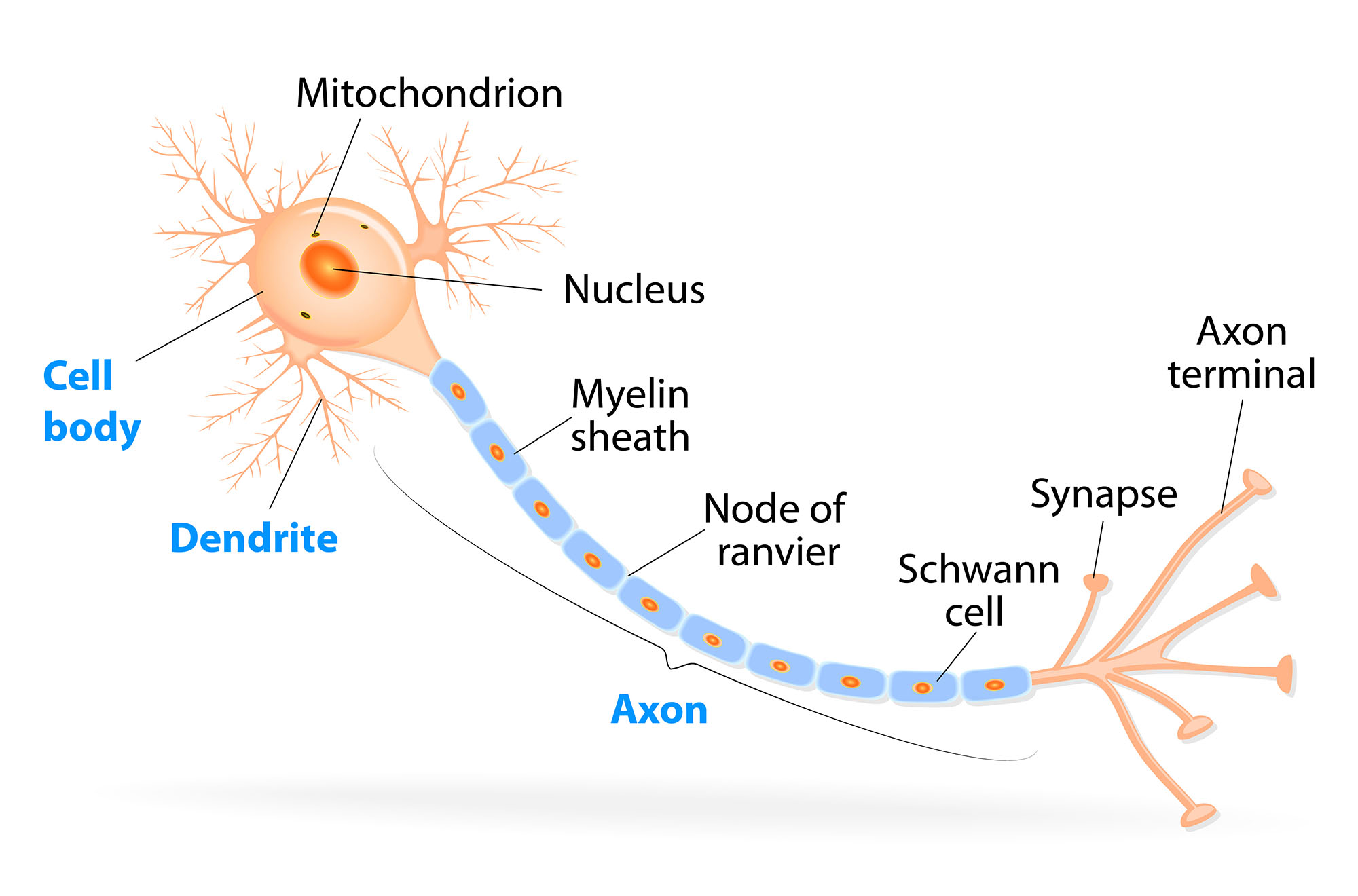
In this longitudinal cut of a nerve, look for the axons and their myelin.
This is a transverse view of a nerve, which is a bundle of _____. What are the circles with “dots” inside of them?
The next section provides examples of how the nervous system works, including impacts on nervous system function.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
list the organs and functions of the central and peripheral parts of the nervous system, including the locations of the sciatic nerves, median & ulnar nerves, and cranial nerves?
-
identify the parts of a neuron in a drawing or microscopic image, including the dendrites, cell body, axon, and myelin?
-
explain what occurs at a synapse when one neuron communicates with another neuron?



