
Urinary Disorders


Urinary Disorder Objectives
-
Describe the types of information provided by urinalysis, including some of the limitations of trying to make diagnoses simply based on urine characteristic.
-
List and describe various kidney diseases, including kidney stones, renal cancer, polycystic disease, and urinary tract infections.
-
Describe liver functions and diseases, including the impact of excessive alcohol consumption.
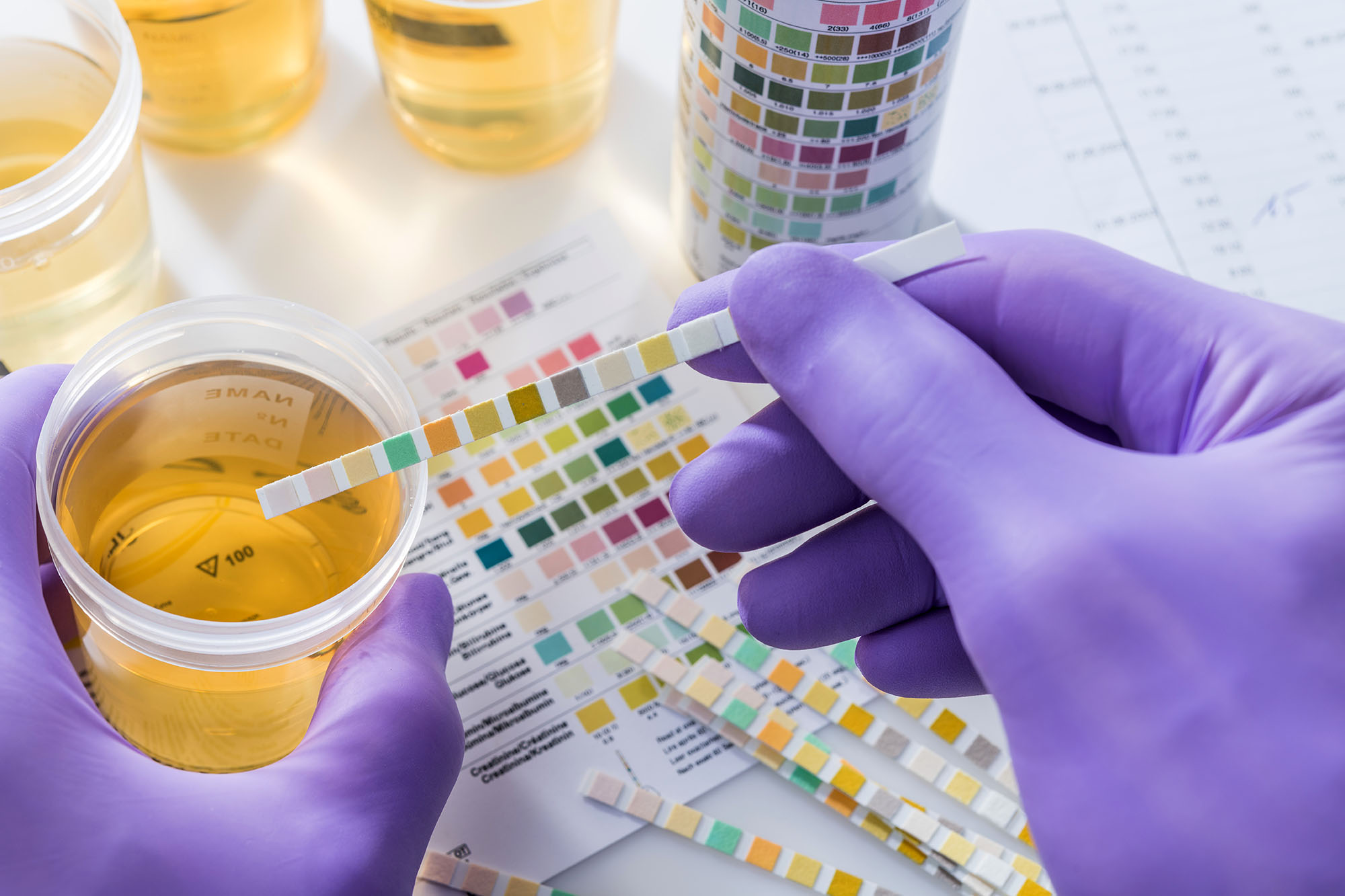
Before we get into disorders specific to the urinary system, we will start with a look at urinalysis, or urine testing, as a technique for diagnosing disease.
Urine testing is done frequently, along with blood testing, to screen for a variety of diseases.
This video demonstrates some of the key characteristics of urinalysis.
Urinalysis may pick up on kidney issues, or other urinary tract disorders like bladder infections. This video introduces some of the more common urinary disorders.
Reduced Filtration
Kidney damage from different disorders can reduce blood plasma filtration. This loss of homeostasis can impact blood pressure, nutrient availability, and a number of other body processes.
Similar to other organs, the kidneys have a suite of diseases that can damage tissue. This video introduces some of these diseases.
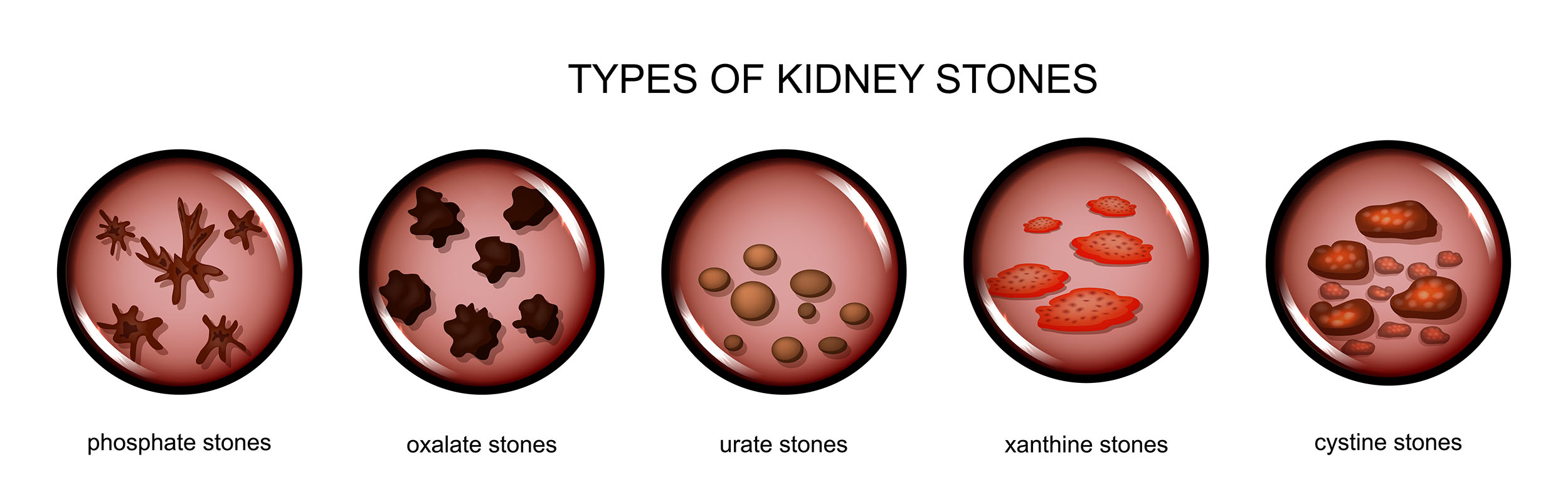
Different types of kidney stones can form depending on the mineral that is crystalizing.
Strange, but true: some people collect different types of kidney stones, kind of like rock collecting.

We have all heard it repeatedly: reduce risk for a variety of diseases by eating a balanced diet, participating in regular exercise, getting enough sleep, and reducing negative stresses. So why are these factors often a lower priority than other things in our lives?
In this section we’ll start talking about risk, and explore information that you can use to make your own daily decisions.
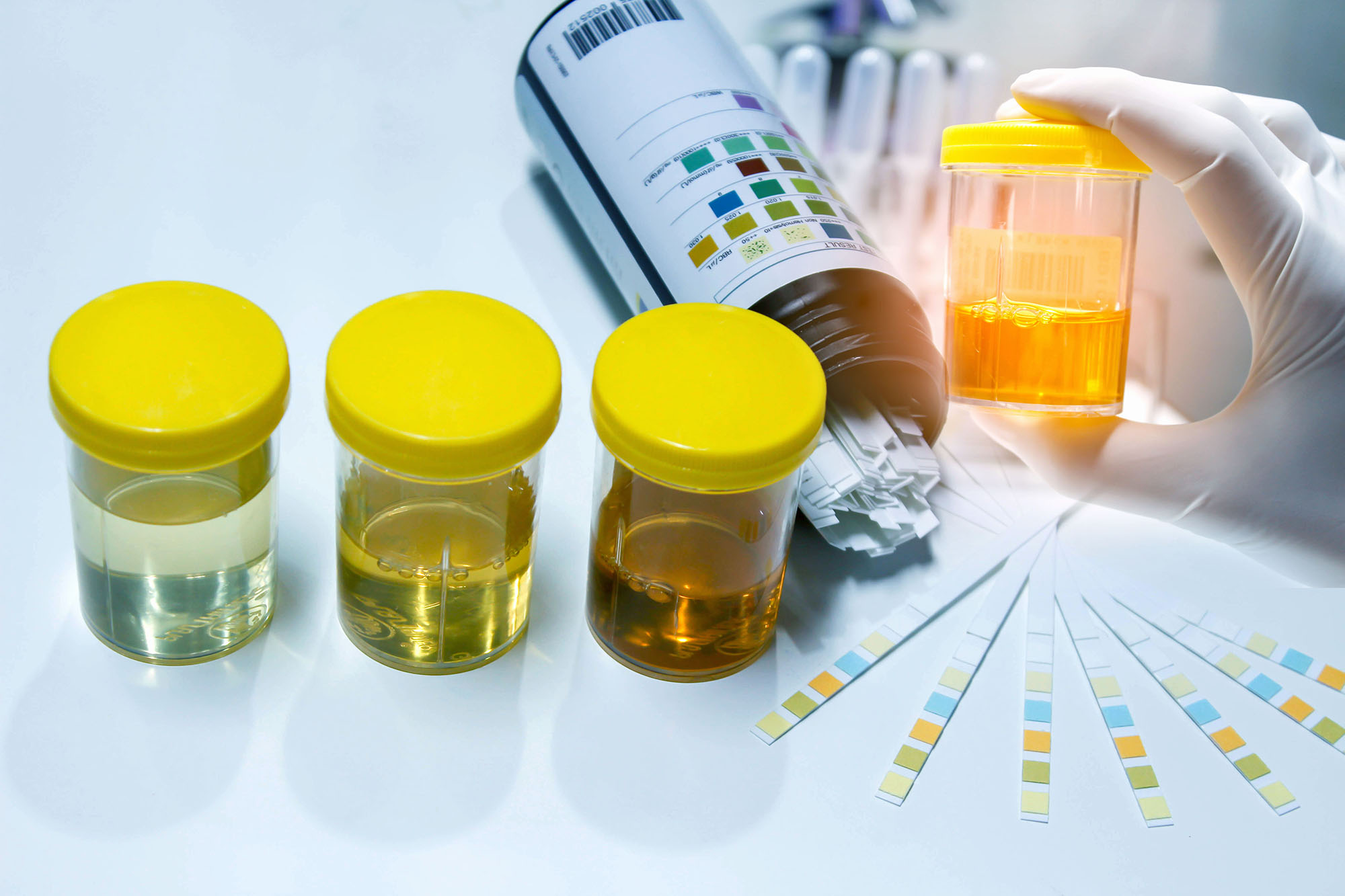
Self-diagnosis is common, but in many cases like urine, it is hard to determine why changes are occurring. Medical personnel have access to wide ranges of testing and knowledge in how to interpret results.
Liver
The liver has come up repeatedly in this course, and we’re going to provide more detail here since it is one of the organs that links together several organ systems.
Liver Damage
This model illustrates some of the more common liver diseases.
Hepatitis & Cirrhosis
Several factors can cause liver inflammation (hepatitis), and over time the liver can scar (cirrhosis).
Excessive Alcohol Impacts
Excessive Alcohol
Alcohol can negatively impact a wide range of organs over time.
Alcohol Poisoning
“Binge” drinking of multiple alcoholic beverages in a row can lead to life-threatening loss of homeostasis.
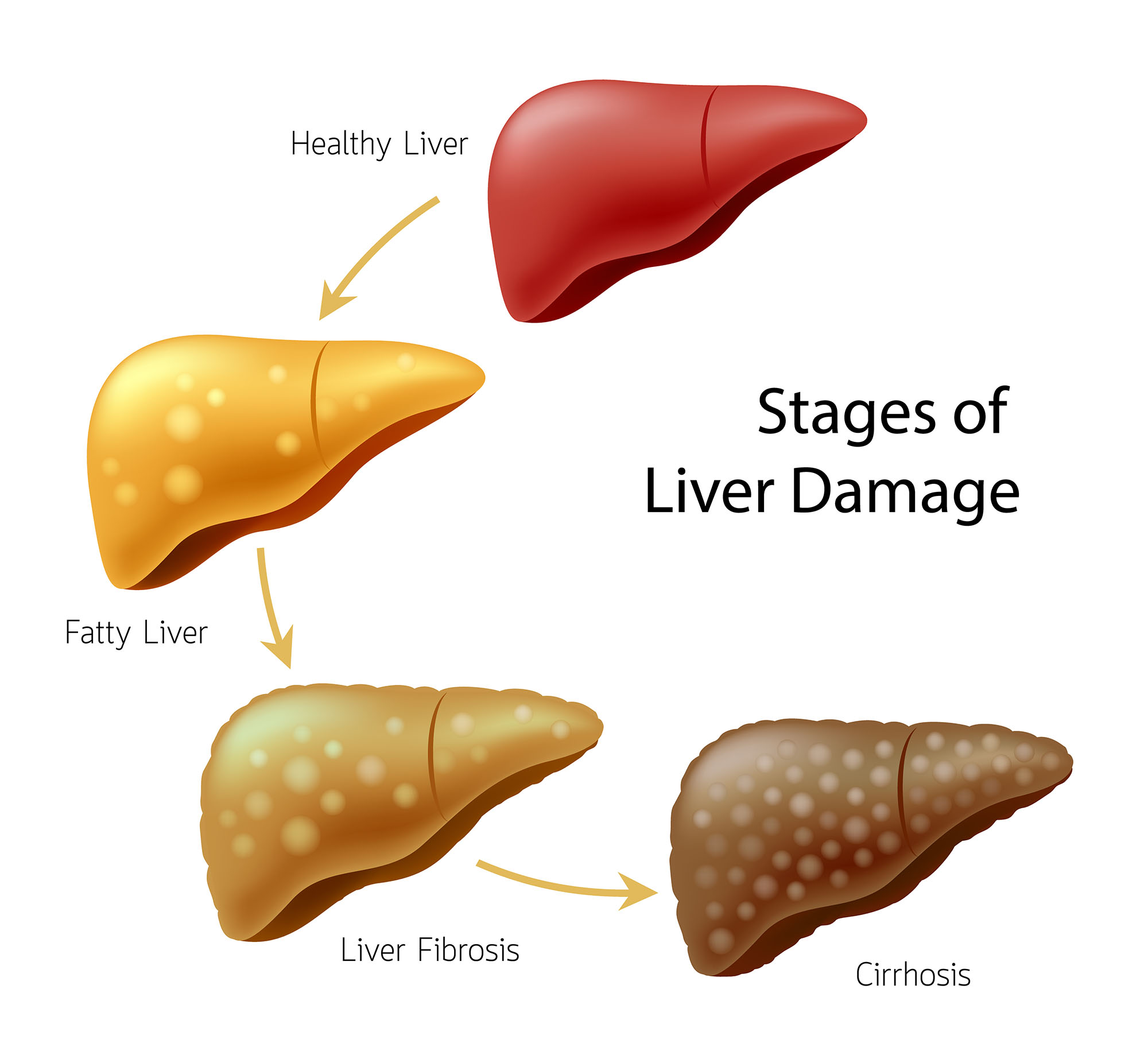
Type 2 Diabetes (covered in an upcoming Guide), obesity, and excessive alcohol consumption can lead to fat building up in the liver. If left untreated, parts of the liver become fibrous and scarred, losing function.
These videos compare normal liver architecture with fatty liver.
The next section introduces the endocrine system and the role of hormones in maintaining homeostasis.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
describe the types of information provided by urinalysis, including some of the limitations of trying to make diagnoses simply based on urine characteristic?
-
list and describe various kidney diseases, including kidney stones, renal cancer, polycystic disease, and urinary tract infections?
-
describe liver functions and diseases, including the impact of excessive alcohol consumption?



