Course Overview Exploring, Describing, & Explaining the Human Body


Course Overview Objectives
- Define the four course topics and explain how biology has a consumer, cultural, and citizenry context.
- Explain the basics of microscope use (microscopy), including history, magnification, and the use of stains.
- Distinguish between the four major types of tissues.
Journal Pages
Journal pages are introduced in each guide
Assignments can be completed with commonly available items
Journal Pages are assembled into a final Biology Journal
Quizzes
Four questions on each quiz
Questions match four outcomes in each guide
Open notes and individual effort
Journaling has a long history in science.
This is a photo of notes the naturalist Charles Darwin made about barnacles, marine organisms with jointed feeding structures. There are images, text, and icons, in this case lines pointing to structures.
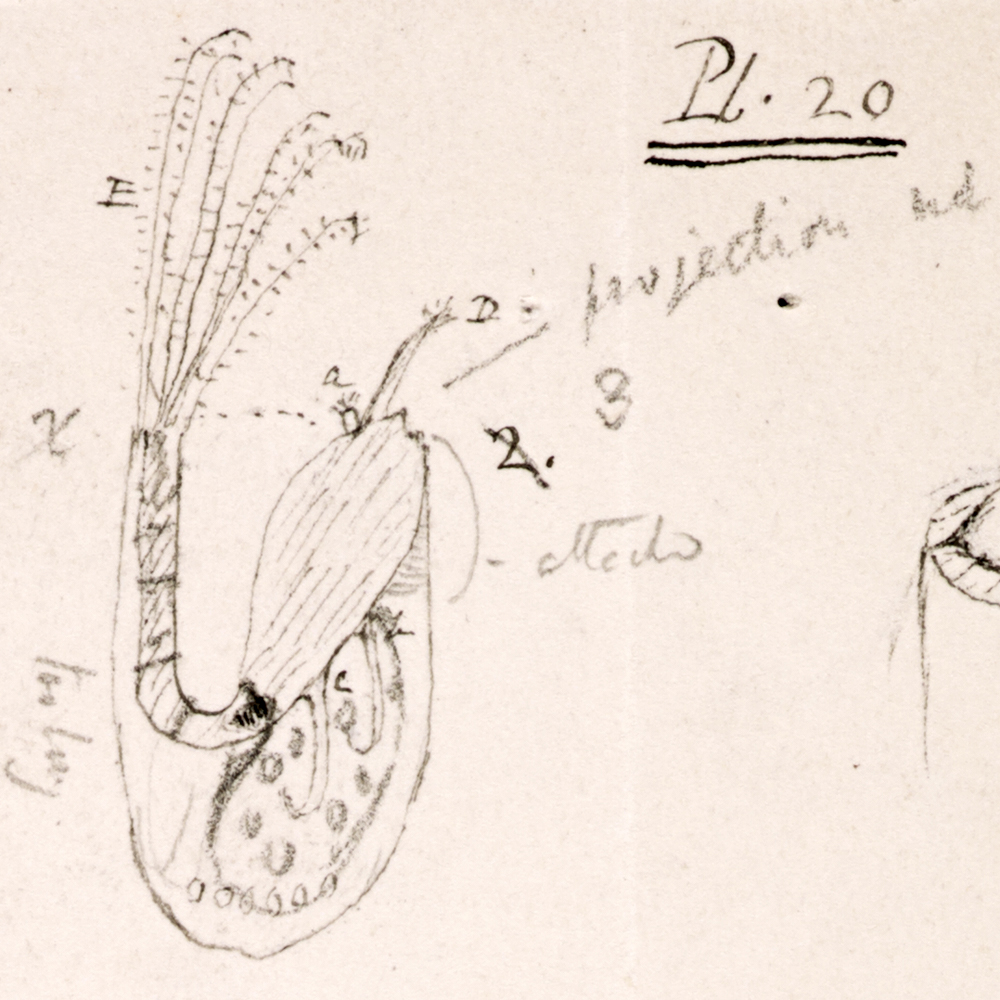
Journaling can be an alternative form of collecting that minimizes impact on organisms and environments.
Contemporary journaling about nature often incorporates found and recycled materials. Some artists produce “junk journals” from a variety of available resources.
You are welcome to use recycled materials in this course’s journal assignments.
Everyone typically develops their own style of journaling. Here are a few personal journals that show variations in journaling.
You can see a few examples of journaling you are doing in this course.
Start your first journal page here
Journal Page #1: Notes
In this section and the next three sections (webpages) of this Organization Guide, you will be taking notes on the concepts that are covered. At the end of the guide, you will upload these notes to Canvas as one of this guide’s two journal assignments.
You can take notes digitally on a device or on a piece of paper that you digitally photograph and upload: your choice. You may have more than one page; take thorough notes because you can use these on the quiz.
We have provided PDF templates of the journal pages on Canvas if you have access to a printer. You do not need to use these; many people like to make their own pages, but also like to see what ours look like.

Include in your notes:
-
concepts from all four sections (web pages) in this guide.
-
a combination of text, images, and icons. Your notes may be mostly text, but some type of image and use of icons needs to be included.



Start your notes here
The following video introduces the course topics and the focus of study within this course. While taking notes, consider that you will be able to use these on this guide’s quiz. Be organized and thorough.
This is a lab course. When you think of a biology lab, what is the main piece of equipment you expect to see?
Whenever there is a photo of paper ephemera from old books and magazines, like this picture, that is a visual cue to back up the verbal cue that you are accessing past experiences and knowledge.
The earliest optical or “light” microscopes date back to the seventeenth century, magnifying specimens beyond the range of normal human vision. Early magnification was approximately 10x, or ten times the unaided eye,
Now microscopes that shine light through specimens can magnify over 1500x and electron microscopes developed in the 20th century magnify 200,000x. Most of the research topics discussed in this course requiring microscopic examination, or “microscopy,” would use an optical “light” microscope.
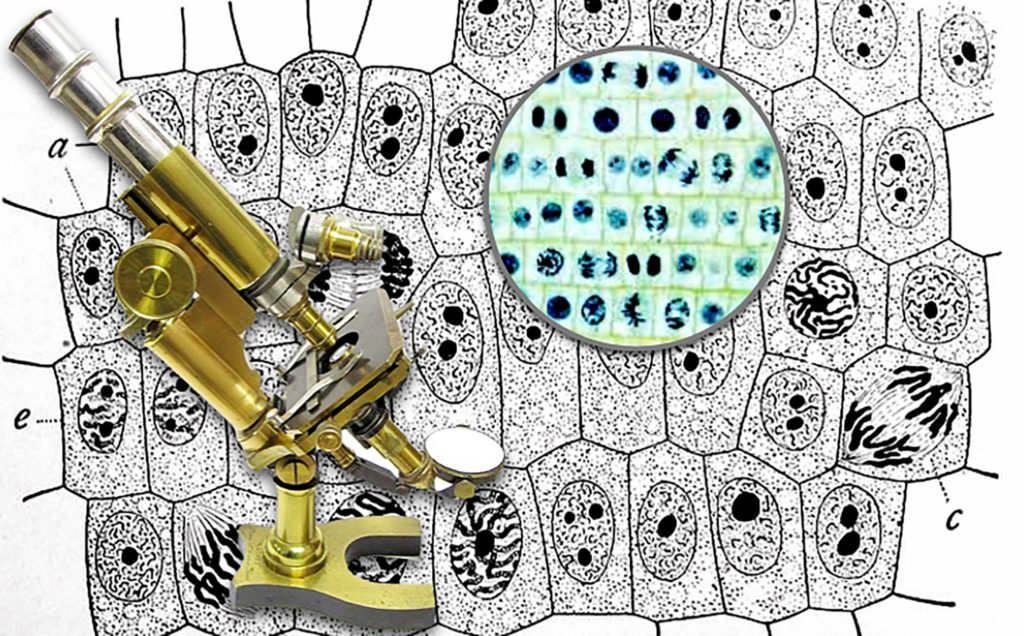
The photos on the right are different high magnification views of a bee.

One consideration in looking at microscope images throughout this course is that you are typically just looking at a small piece of a larger specimen.
Total magnification is the magnification of the eyepiece times (x) the magnification of the objective being used.
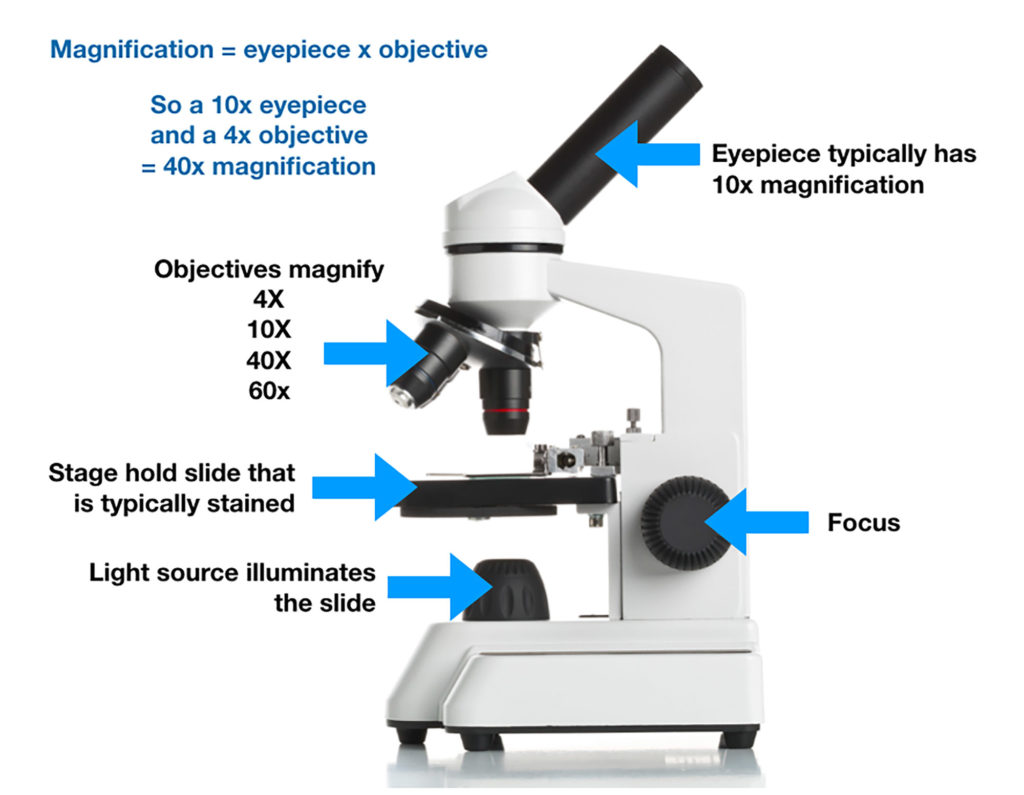
A bright light shines through a thin tissue of cells and finely ground glasses magnify the image. Both the eye pieces and specialized lenses called “objectives” magnify. From this image, if you have a 10x eye piece and a 10x objective, what is the total magnification?
answer: 100x
Studying Cells with Microscopes
Here are a few basics on glass lenses and light sources in microscopes, as well as staining of animal tissues (groups of cells) in microscope slide preparation. The slides used come from a variety of animals; many have cells similar to humans.
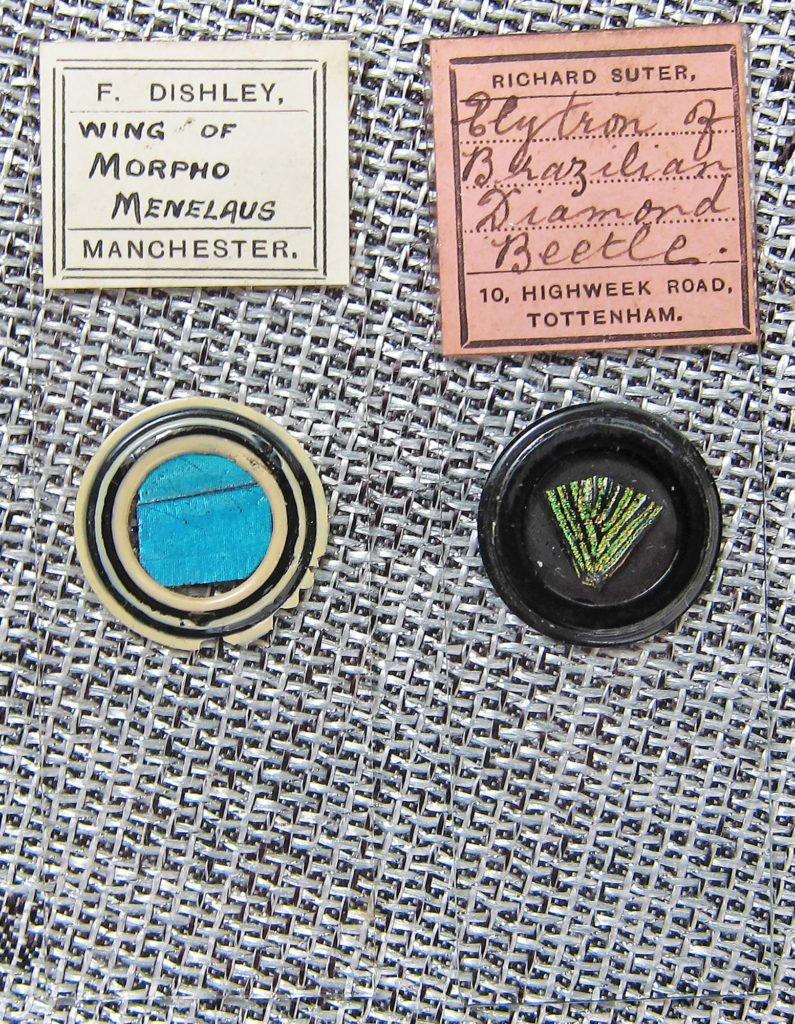
Antique microscope slides were frequently prepared with chemicals that are now known carcinogens (cancer-causing agents), that are no longer used. Unfortunately the high quality coloring and contrast produced by these stains has not been fully replicated.
This video shows examples of dramatically different stains from an antique slide collection.
Stains can turn clear cells that are difficult to read into powerful sources of information. Using a medical example, women get regular pap smears to detect possible abnormal growth in the cells lining the cervix. These cells are colorless under bright light until stain is added.
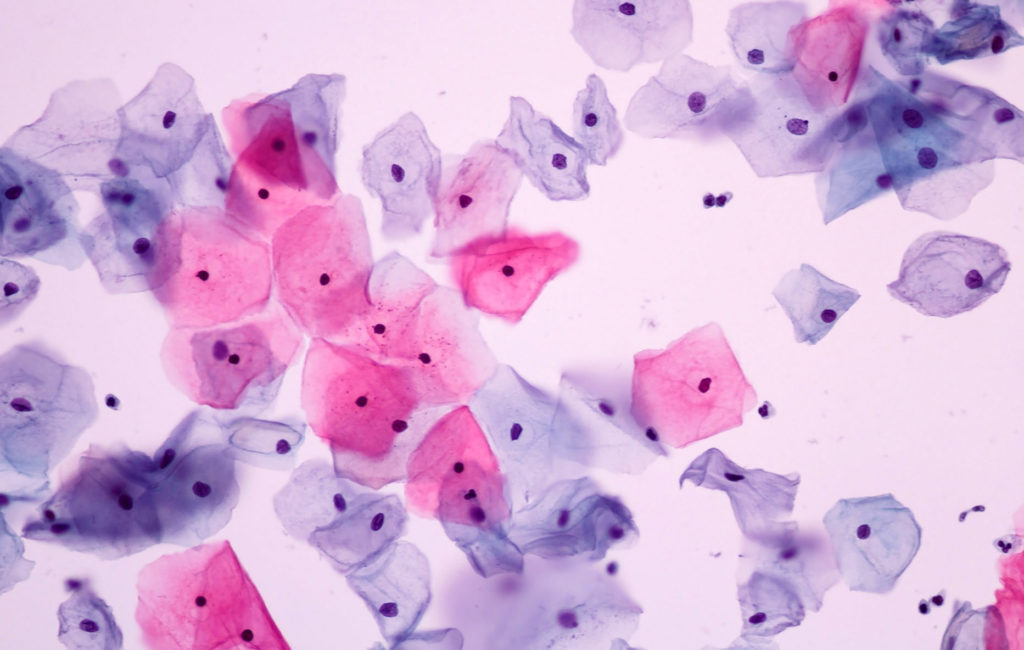
Normal Cells 200x
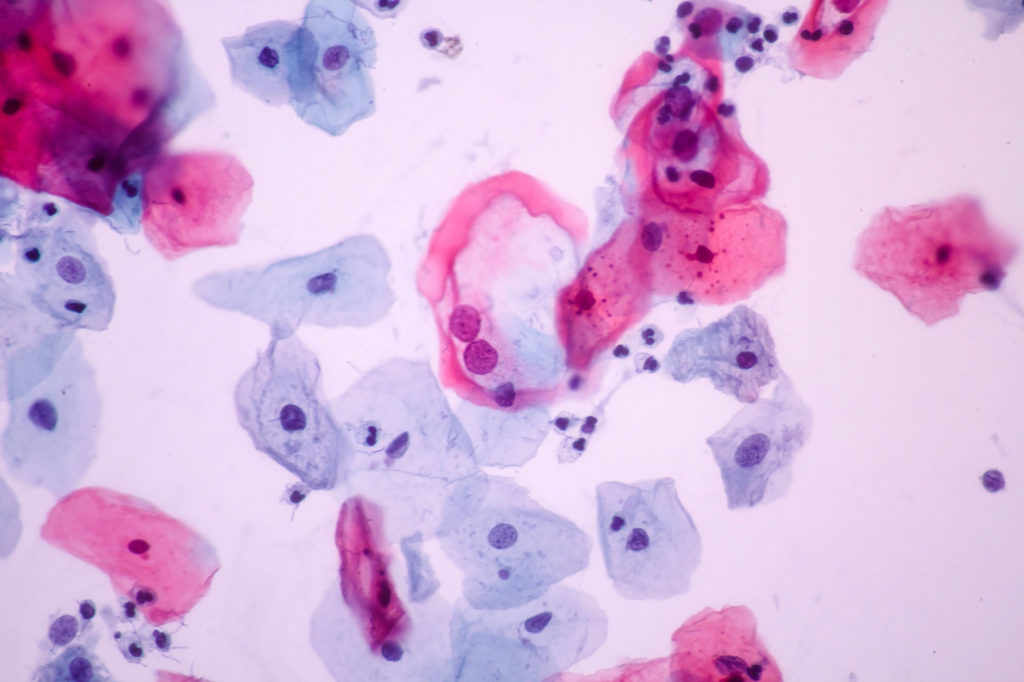
Abnormal Cells 200x
Types of Tissues
This video introduces cells and tissues (groups of cells) that are visible with a microscope.
A ______ is a group of cells, like this group of fat cells (adipocytes).


What are the functions of each of these four general tissue types in the human body?

What is a misconception?
Why is thinking that eating a completely fat-free diet a misconception?
The next section provides details on cellular structures and functions.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
- define the four course topics and explain how biology has a consumer, cultural, and citizenry context?
- explain the basics of microscope use (microscopy), including history, magnification, and the use of stains?
- distinguish between the four major types of tissues?




