
Respiratory Disorders


Respiratory Disorder Objectives
- Describe pneumonia and COPDs, including chronic bronchitis, asthma, and emphysema.
-
List and describe diseases that may result from smoking cigarettes.
-
Explain the breathing process including muscle movement, lung capacity, and the impacts of aerobic exercise.
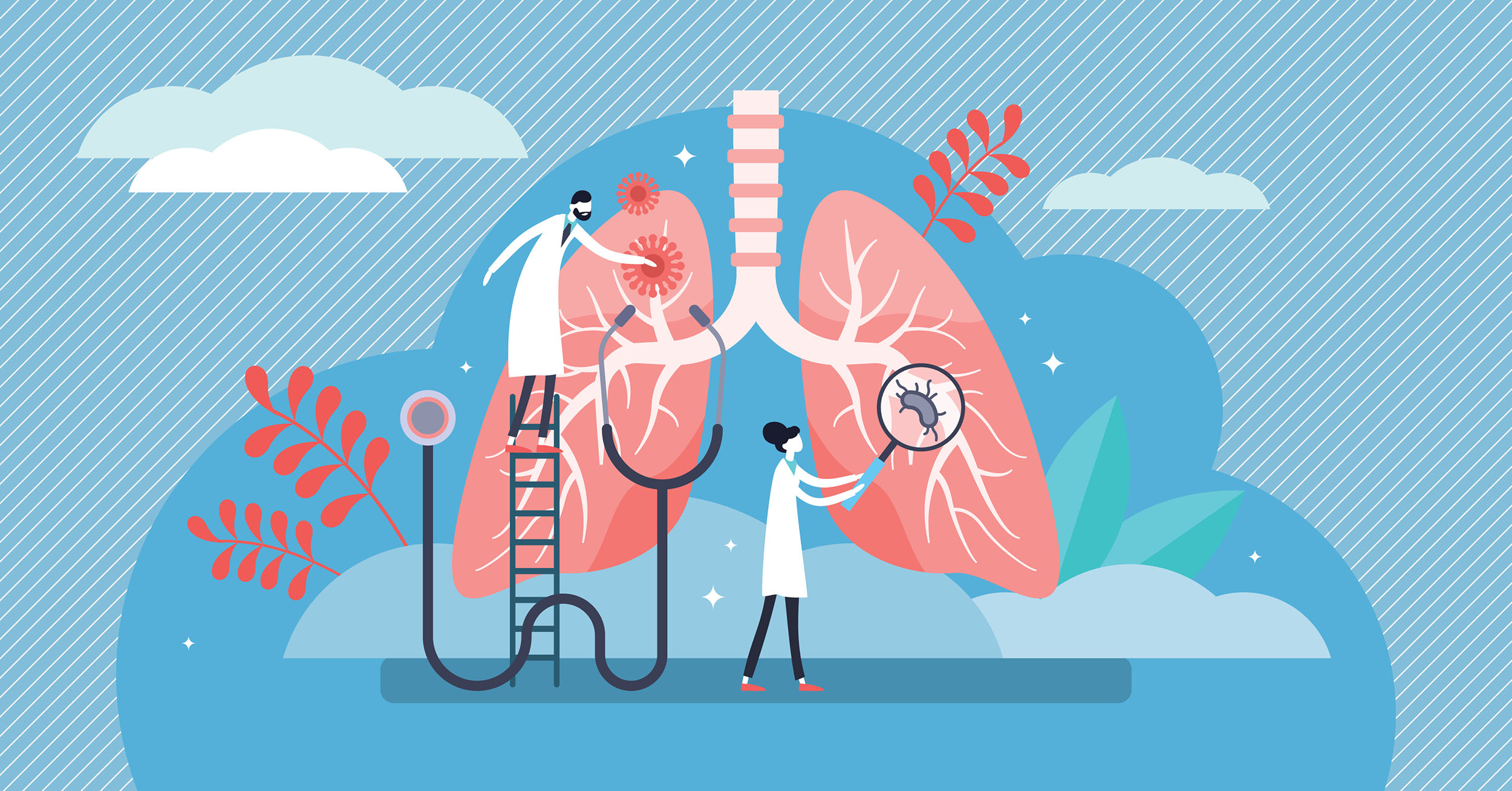
Homeostasis is maintaining relative balance in the body. Disease is a loss of homeostasis. Unfortunately, the human respiratory system can develop several significant disorders.
We will start with an overview of respiratory disorders.
This model provides an idea of the range of disease that can occur in the lungs.
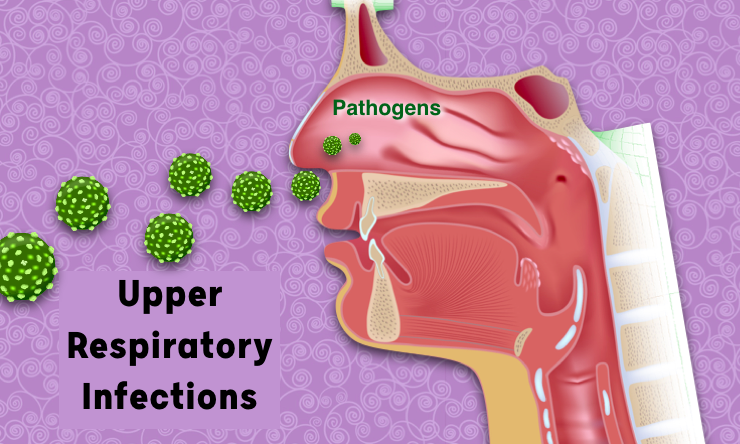
It is relatively easy to inhale bacteria and viruses that cause infections in the nose, throat, and sinuses. However, most of these upper respiratory infections are not fatal.
Lower respiratory diseases within the lungs can be difficult to detect and treat.
Pathogens and a variety of non-infectious disease like cancer can lead to pneumonia, excessive inflammation in the lungs. Fluid blocks air movement in the alveoli. The body is trying to fight off a perceived threat, but this response can be fatal.
There are also serious chronic (long-term) lower respiratory diseases, including chronic bronchitis, asthma, and emphysema.
This model demonstrates that COPDs can dramatically reduce respiratory capacity.
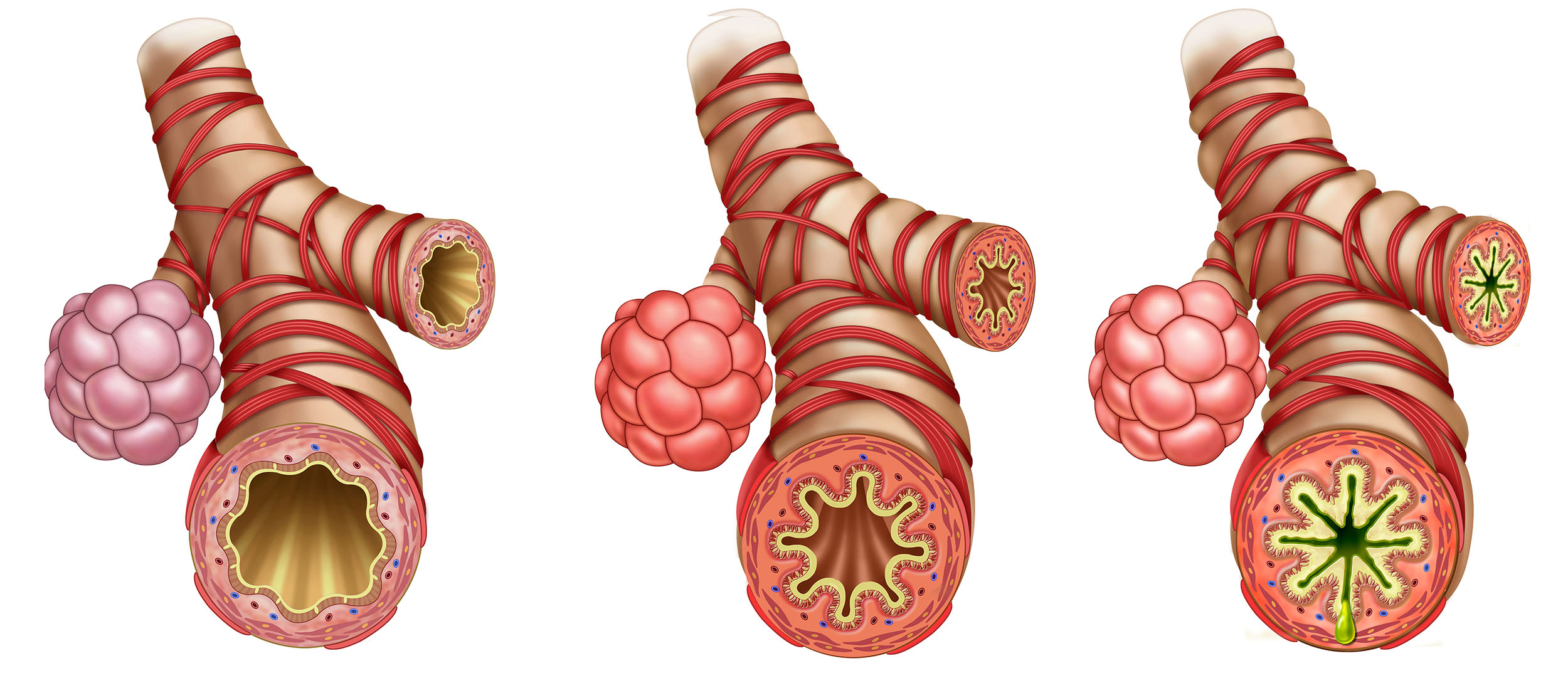
Asthma can inflame and constrict bronchioles, blocking air flow.
Cigarette smoking has multiple impacts on respiratory health.
Cigarette smoking has been shown to cause emphysema and lung cancer in laboratory animals, but in humans we hear about a correlation (relationship) between smoking cigarettes and diseases. What was done with laboratory animals that we are unlikely to do with people?
Answer: experiment, altering variables to show cause and effect
To show the severity of lung diseases, this video provides a microscopic view of pneumonia, emphysema, and cancer.
We all know we’re supposed to exercise regularly. Understanding the biological impact of aerobic exercise on the heart can be motivating to keep moving.
Breathing is movement, and it involves two groups of muscles: the intercostal (rib) muscles) and the large diaphragm that separates the chest (thoracic) and abdominal body cavities.
Yawning
Heimlich Maneuver
Exercise increases breathing muscle strength and the amount of air that enters alveoli when inhaling. This results in increased oxygen in the blood and cells throughout the body.
You can measure lung capacity, and monitor changes, with a spirometer.
If you have ever been in the hospital for a while and have experienced a decline in respiratory capacity, you may have been sent home with a device like this.
This is the end of Guide 3’s content. After you check your knowledge over the material, proceed to the product page.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
- describe pneumonia and COPDs, including chronic bronchitis, asthma, and emphysema?
-
list and describe diseases that may result from smoking cigarettes?
-
explain the breathing process including muscle movement, lung capacity, and the impacts of aerobic exercise?



